tags : Systems
# good place to learn about ELF
$ man elfIn computing, the Executable and Linkable Format (ELF, formerly named Extensible Linking Format), is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps. There are many different ABI formats but ELF is the preferred format since it is flexible and extensible by design, and it is not bound to any particular processor or architecture
Structure
The structure of ELF consists of the ELF Header and the rest of File data.
Only the ELF header has a fixed position in the file. Not all sections in the ELF are necessary, there are some ELF sections which are exec obj specific, some are debugging specific etc. The flexibility of the ELF format requires no specified order for header tables, sections or segments. However, this figure is typical of the layout used in Solaris.
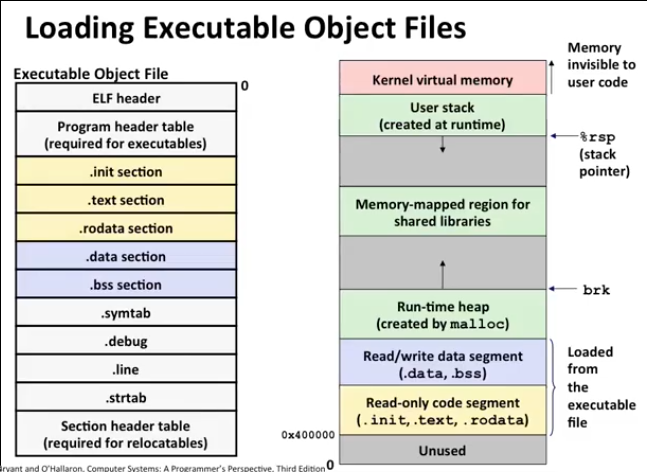
ELF Header
Contains all kinds of information about the ELF file like its Class(ELF32=/=ELF64), Types(ET_REL,=ET_EXEC=,=ET_DYN=,=ET_CORE=) etc.
File Data
- Program header table(PHT) : A list of segment headers, required for executables. This table tells the system how to create a process image. Files used to generate a process image, executables and shared objects, must have a PHT; relocatable objects do not need such a table.
- Section header table : A list of section headers. Every section has an entry in this table. Each entry gives information such as the section name, the section size, and so forth. Files used in link-editing must have a section header table; other object files might or might not have one.
- Rest of the file contains data pointed to by the above two headers.
Tools
- All the binary utilities GNU provides, Binutils.
nm,size,file,execstack,readelf,ldd,hexdump,objdump,elfedit
- The ELFUtils tools. : The tools from elfutils were written to be smaller, faster, and more featureful than those in binutils.
- A stripped ELF will lack a .symtab entry. The file command traverses through all the ELF section headers until a symbol table section is found. If one cannot be found, the binary is considered stripped.
A lot of the tools used to inspect ELF files sort of do the same thing and same results can be found by using proper flags.
Doubts
- What is
@progbits
Section and Segments
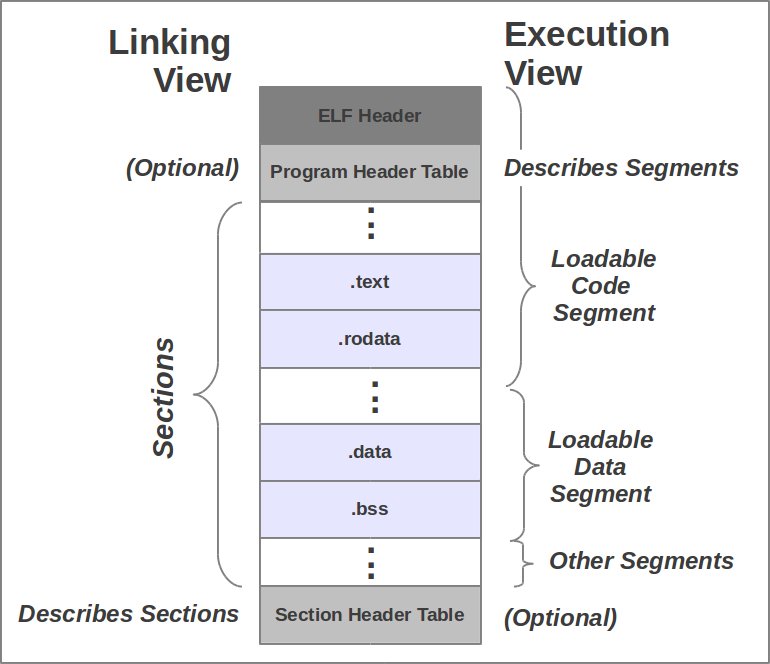
sectionslive insidesegmentssectionscontain information needed duringlinking(Linker cares)segmentscontain information needed at runtime (Loader cares)
# mapping of sections to segments
# output is trimmed
$ readelf -l a.out
Elf file type is DYN (Shared object file)
Entry point 0x1020
There are 11 program headers, starting at offset 64
Program Headers:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr
FileSiz MemSiz Flags Align
PHDR 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040
0x0000000000000268 0x0000000000000268 R 0x8
INTERP 0x00000000000002a8 0x00000000000002a8 0x00000000000002a8
0x000000000000001c 0x000000000000001c R 0x1
[Requesting program interpreter: /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2]
LOAD 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
...
0x0000000000000200 0x0000000000000208 RW 0x1000
DYNAMIC 0x0000000000002e38 0x0000000000003e38 0x0000000000003e38
0x00000000000001a0 0x00000000000001a0 RW 0x8
NOTE 0x00000000000002c4 0x00000000000002c4 0x00000000000002c4
0x0000000000000044 0x0000000000000044 R 0x4
GNU_EH_FRAME 0x0000000000002004 0x0000000000002004 0x0000000000002004
...
Section to Segment mapping:
Segment Sections...
00
01 .interp
02 .interp .note.gnu.build-id .note.ABI-tag .gnu.hash .dynsym .dynstr .gnu.version .gnu.version_r .rela.dyn
03 .init .text .fini
04 .rodata .eh_frame_hdr .eh_frame
05 .init_array .fini_array .dynamic .got .got.plt .data .bss
06 .dynamic
07 .note.gnu.build-id .note.ABI-tag
08 .eh_frame_hdr
09
10 .init_array .fini_array .dynamic .gotWe can create our own sections in the assembly file
Section
- Sections live in object files (
.o) and represents the smallest units that can be processed within an ELF file. - They hold the bulk of object file information for the linking view: instructions, data, symbol table, relocation information, and so on.
- One of the section
.symtabcontaines the symbol table which the linker needs to do linking.
Segments
- Segments are a collections of
sections(0 or more)- It is the smallest individual units that can be mapped to a memory image by loader or by the runtime linker.
- When you link multiple objects together to make an executable
- Sections get put into segments.
- ELF binary files consist of
- The ELF header
- Segments
Executables still can also contain sections, but that information is only useful for debugging: it can be stripped and it will still run just fine.
The operating system copies the segment (if it is loadable, i.e., if p_type is PT_LOAD) into memory according to the location and size information.
- The
.textsection contains executable code and is packed into a segment which has the read and execute access rights. - The
.dataand.bsssections contain initialized and uninitialized data respectively, and are packed into a segment which has the read and write access rights.
Allocable and a non-allocable ELF sections
TODO