tags : Systems
The agreement between the two computers about the correspondence between letters and numbers is what Unicode standardizes.
In terms of Unicode,
his:
- An
abstract characternamedLATIN SMALL LETTER H.- This
characterhas the correspondingnumber 0x68- Which is a
code pointin notationU+0068.
- The first Unicode version 1.0 was published in October 1991 and had 7,161 characters “associated”. The latest version provides codes for 149,186 characters “associated”.
- Total characters: 216 + 220 - 211 = 1,112,064(~1mn) assignable code points.
- 216 : Plane 0 (BMP) (
U+0000-U+FFFF) - 220 : Plane 1-16 (astral planes/supplementary planes) (
U+10000-U+10FFFF) - 211 : Code points from
U+D800-U+DFFFwhich are used to encode surrogate pairs inUTF-16
- 216 : Plane 0 (BMP) (
Codespace and blocks
- The Unicode
codespaceis divided into 17planes, numbered 0 to 16. - The Unicode Standard defines a
codespace(a set of numerical values ranging from 0 through 10FFFF) calledcode pointsand denoted asU+0000throughU+10FFFF(See blocks.txt ) - Plane 0 is the
Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP)- Single code unit in
UTF-16encoding - Encoded in 1, 2 or 3 bytes in
UTF-8.
- Single code unit in
- Planes 1 through 16 are supplementary planes
- Accessed as surrogate pairs in
UTF-16 - Encoded in four bytes in
UTF-8
- Accessed as surrogate pairs in
- Within each
plane, characters are allocated within namedblocksof related characters.- Characters required for a given script may be spread out over several different blocks.
Code units
How unicode is interpreted by the computer: code units
Code unit is a bit sequence used to encode each character within a given encoding form.
- The
character encodingis what transforms abstract code points into physical bits: code units. - Popular encodings are
UTF-8,UTF-16andUTF-32(UTF = Unicode Transformation Format)
Encodings
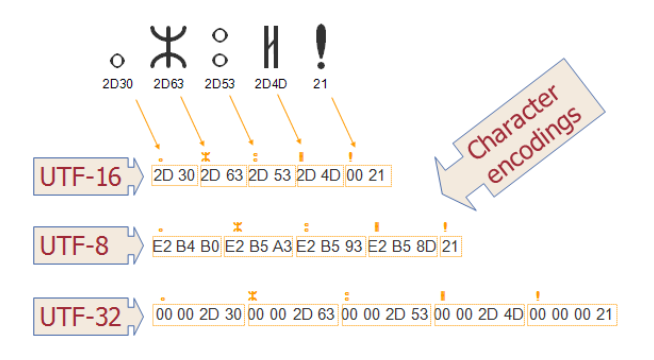
UTF-16
- Windows tends to use UTF-16
- It uses 16 bit code units (16 bits = 2 bytes).
- variable-length encoding
- Surrogate pairs are a UTF-16 thing.
- The main hazard of UTF-16 is that it leads to people believing they are handling unicode correctly, when often they don’t properly decode surrogate pairs, etc.
- Surrogate pair is a representation for a single abstract character that consists of a sequence of code units of two 16-bit code units, where the first value of the pair is a high-surrogate code unit and the second value is a low-surrogate code unit.
- Code points
- Code points from BMP are encoded using a single code unit of 16-bit
- Code points from astral planes are encoded using two code units of 16-bit each(U+D800 - U+DFFF). (surrogate pairs) This allows encoding of over one million additional characters.
- High surrogate: Unicode code point from range U+D800 to U+DBFF gets combined with another unicode code point
- Low surrogate: Unicode code point from range U+DC00 to U+DFFF to generate a whole new character
UTF-32
- It uses 32 bit code units (32 bits = 4 bytes).
- An encoding where “all characters [are] matched with just one code point”, and it’s UTF-32.
- Pros
- character is the same length. (fixed length encoding). So you know right away where you can split it without cutting any letters in half.
- Cons
- Takes too much space. i.e downloading that text takes four times as long compared to UTF-8.
UTF-8
- Mac OS X and Linux use UTF-8.
- variable-length encoding
- It uses 8 bit code units (8 bits = 1 byte).
- It uses sequences of
up to four code unitsto encode onecode point. - Pros
- UTF-8 has the advantage that it uses the least amount of space if your characters are mostly in the basic Latin alphabet and punctuation. Webpages use UTF-8 because of this.
- Cons
- If you want to split the text into pieces, you have to be careful not to break up the text in the middle of a character.
- It’s also not possible to find the 100th character without going through the first 99 (since they could be different lengths).
Language usage
Javascript
Stringsare represented fundamentally as sequences ofUTF-16code units.- every code unit is exact 16 bits long. (maximum of 216, or
65,536possible characters) - This character set is called the basic multilingual plane (BMP)
- To avoid ambiguity, the two parts of the pair must be between
0xD800and0xDFFF, and these code units are not used to encode single-code-unit characters.splitby UTF-16 code units and will separate surrogate pairs.
- Surrogate pairs, combining marks and grapheme are tough to handle in JavaScript.
- Where ECMAScript operations interpret String values, each element is interpreted as a single UTF-16 code unit. i.e The length of a String is the number of elements. always think of string in JavaScript as a sequence of code units.
- Most of the JavaScript string methods are not Unicode-aware.
- What every JavaScript developer should know about Unicode
- Every element of a string is interpreted by the engine as a code unit.
- The way a string is rendered does not provide a deterministic way to decide what code units (that represent code points) it contains.
console.log('cafe\u0301'); // => 'café'
console.log('café'); // => 'café'
// 'cafe\u0301' and 'café' literals have slightly different code units,
// but both are rendered the same sequence of symbols café.Escape sequences
Escape sequences in strings are used to express code units based on code point numbers.
- Hexadecimal escape sequence
- Unicode escape sequence
- Code point escape sequence(new)