tags : Web Development, Javascript Runtime and Browser, Javascript
Basics
Example Usage
- Ad and Tracking Blockers
- PW Managers
- Smart Writing Management Tools
- Accessibility Tools
- Content and Link Aggregators
- Tab mgmt
- Screen Rec
- Devtools
Extension Model (Where it places)
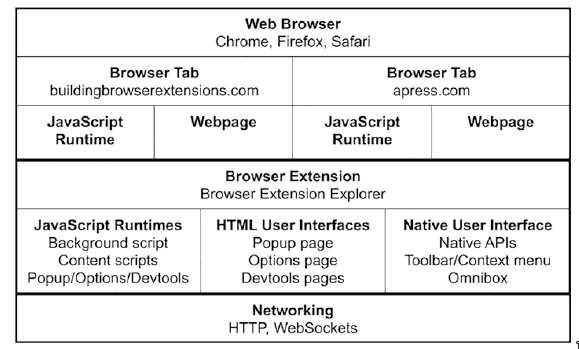
- From the perspective of the web page, browser extensions can be thought of as an invisible supplemental entity.
- Own
- Own runtime
- Render pages in their own sandboxed contexts
- Own APIs
content scriptsare exceptions.- Web page and extension can access DOM & Share resources
- Extension specific sandboxing
What extension can offer
-
UI
Each of the following pages are rendered as any normal webpage with events, own Runtime and DOM etc.
- Popup page
- Options page
- Devtools page
-
Non-UI
These don’t have UI but have their own Javascript Runtime
- Background script
- Content script
Lifecycle
- Not restricted to single source. (Given enough permission, it’ll be able to access all tabs)
- Can exist without any webpage open at all. (Exception:
content scripts,devtool pageetc)
Components
The most basic extension will need a ext manifest and background script at min.
Extension Manifest
-
v2
- Background script had the option of being either
- Persistent: Background script is initialized exactly once and lives in memory until the browser is closed
- Non-Persistent: Background script exists as an
event pagethat is initialized on demand whenever a relevant browser event occurs.
- Background script had the option of being either
-
v3
background scriptexist as service worker (See Web Performance), similar tov2-non-persistent
Background Script
- Function: Handle browser events
- Extension lifecycle events: Eg. install or uninstall
- Browser events: Eg. navigating to a web page or adding a new bookmark
- Abilities
- Access the WebExtensions APIs
- Performing actions such as exchanging messages with other parts of the same extension
- Exchanging messages with other extensions
- Programmatically injecting
content scriptsinto a page
Pages
-
Popup Page
- Concerns
- Cannot be opened programatically
- Abilities
- Access the WebExtensions APIs
- Concerns
-
Options page
Display a custom user interface. The options page behaves as a standalone web page that opens when the user clicks “Options” in the extension toolbar context menu.
- Abilities
- Access the WebExtensions APIs
- Abilities
Injecting
Can inject JS/CSS or both
-
content script
- Sandboxed runtime: can’t read JS properties from web page runtime
- Shares access to the same DOM as the web page itself, so can manipulate the DOM of the webpage.
- Ability
- Limited access to the WebExtensions APIs (Indirect access via messages)
- Can exchanges messages with other extension elements like background scripts.
- declaratively via manifest
- programatically via ext. page
- programatically via background script using WebExtAPI
FAQ
WebAssembly and ManifestV3
- See Sample: Using WASM in Manifest V3 · Issue #775 · GoogleChrome/chrome-extensions-samples · GitHub