tags : Network Programming, Networking, NAT, Packet Analysis
TODO FAQ
IP and TCP/UDP
- IP
- Naming scheme
host-to-host
- UDP
process-to-process
- TCP
process-to-processoverconnectionsusingbyte streams
TODO Stream vs Packet
- TCP/IP is stream-oriented
- Segment??
- UDP is packet-oriented
TODO Segment vs Packets vs Frames
- TCP sends segments
- IP sends packets
- Ethernet sends frames
- See tcpip - What’s the difference between a TCP segment and a TCP packet? - Super…
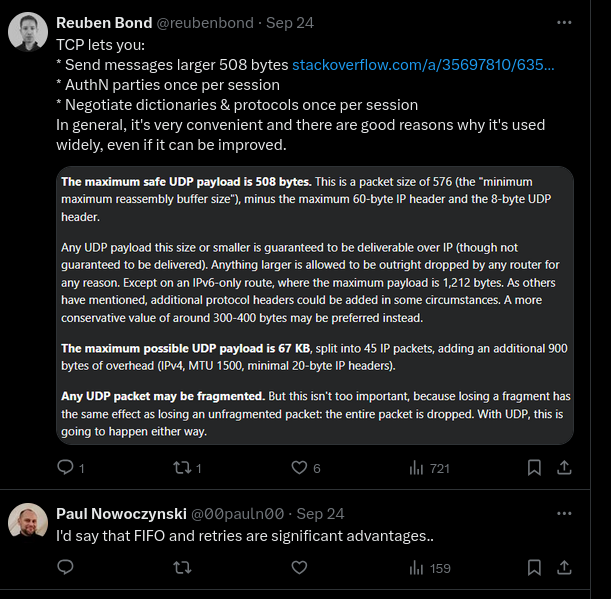
TODO Missing Segments in TCP
- Single segment: (Eg. no more data to send), and that packet s lost, the sender will eventually time out and resend the segment. There’s no way for the receiver to know that there was a segment in flight, so it can’t tell you that it didn’t get it.
- Multiple segments
- One in the middle has been lost
- Receiver will send out an ACK for every new segment
- ACK: highest octet of the segment that
arrived in sequence - Eg. Sender transmits
1460 octet segmentswith initial seq no. of1, 1461, 2921, 4380, and 5840, and the2921segment gets lost, it send backACK of (2920, 2920, 2920, 2920). - First segment skipped because of delatyed ACK (???)
- ACK: highest octet of the segment that
- So it’ll detect duplicate ACKs and retransmit missing segments.
Selective ACK(SACK)can also help here.
TODO TCP Handshake?
TODO UDP is connectionless, but UDP has connection tuple?
TCP
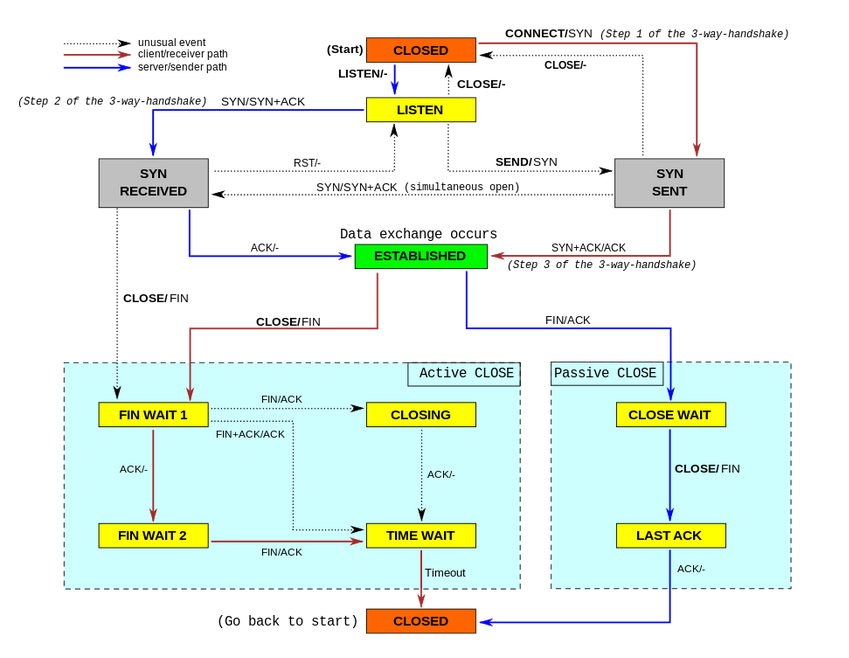
- Connection:
4-tuple{s_ip, s_port, d_ip, d_port}
Handshake
Resources
- When TCP sockets refuse to die
- Making connections with TCP and Sockets for Workers
- What they mostly should know: TCP provides a bidirectional stream of bytes on…
- sockets - Is TCP bidirectional or full-duplex? - Stack Overflow
- it is bidirectional
- it supports full-duplex, duplex is property of phy layer not of tcp
UDP
- Connected sockets:
4-tuple{s_ip, s_port, d_ip, d_port}- Mostly used for outgoing flows
- Unconnected sockets:
2-tuple{bind_ip, bind_port}- Mostly used for inbound server-side stuff
Resources
- A small warning about UDP based protocols | Hacker News
- UDP protocols prone to amplification attacks
- Everything you ever wanted to know about UDP sockets but were afraid to ask