tags : Math, Fixed Point
The term floating point refers to the fact that the number’s radix point can “float” anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating-point can be considered a form of scientific notation.
Introduction
FP are just scientific notion
Advantage
- Speed: Commonly measured in terms of
FLOPS. (Okay THIS MIGHT BE WRONG)# int Integer add: 1 cycle 32-bit integer multiply: 10 cycles 64-bit integer multiply: 20 cycles 32-bit integer divide: 69 cycles 64-bit integer divide: 133 cycles # float Floating point add: 4 cycles Floating point multiply: 7 cycles Double precision multiply: 8 cycles Floating point divide: 23 cycles Double precision divide: 36 cycles source: http://www.phys.ufl.edu/~coldwell/MultiplePrecision/fpvsintmult.htm - Efficiency : Can deal with really big and small numbers without needing large amount of space.
How
Without FPU
A floating-point unit(FPU) is a part of the processor specifically designed to carry out floating-point numbers ops.
With FPU
Bases
- In practice, most floating-point numbers use
base 2, thoughbase10(decimal floating point) is also common, there are also other bases used for FP. - The base determines the fractions that can be represented
1/5cannot be represented exactly as a floating-point number using abinarybase1/5can be represented exactly using adecimalbase (0.2, or 2×10-1)1/3cannot be represented exactly usingbinaryordecimalbase1/3can be represented exactly using base 3 (0.1, or 1×3-1)
Anatomy
A floating-point format is specified by
- Base (radix):
b- Precision:
p(significand, i think)- Exponent range:
emintoemax, wemin = 1 − emaxfor all IEEE 754
Significand
A signed (+/-) digit string of a given length in a given base(radix).
- This digit string is referred to as the
significand,mantissa, orcoefficient. - The
radix(base)point position is always somewhere within thesignificand - The length of the
significand determines the precisionto which numbers can be represented. - Eg.
p=24,b=2, single-precision(32bit) :significandwill bestringof 24 bits. So precision will be till 24bits.
Exponent
- A signed integer exponent (also referred to as the
characteristic, orscale) - Modifies the magnitude of the number.
- eg. -5 is smaller than 3 but greater in magnitude than 3 (-5+3=-2)
- The exponent shifts the radix point in the significand and changes the magnitude
Rounding and Error
Associativity and Commutativity
It’s not associative, not commutative
octave:1> x=0.1+0.2+0.3
x = 0.60000
octave:2> y=0.3+0.2+0.1
y = 0.60000
octave:3> x==y
ans = 0
octave:4> x-y
ans = 1.1102e-16Deterministic?
- They’re deterministic but partially implementation defined.
- Some instructions don’t guarantee the maximum possible precision, and implementations can differ in the least significant bits of their result.
- There are minor differences between hardware (x87 vs SSE is the most famous one, but there are others). Changing compiler, its version or options may produce subtly different results (the most obvious example is the -ffast-math flag). And even the bigger problem is implementation of non-primitive (e.g. trigonometric) functions. Usually your program will use implementation from a system or vendor library, which probably have different underlying implementations.
Precision (based on IEEE 754)
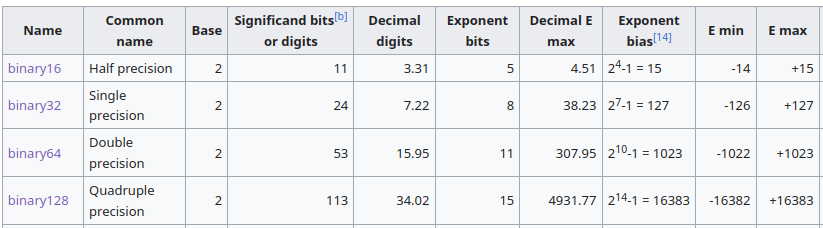
16-bit: Half (binary16)
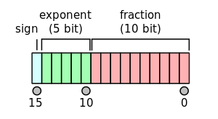
32-bit: Single (binary32)
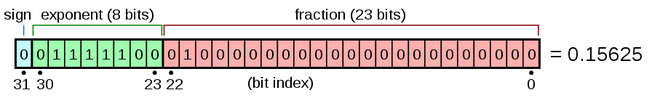
64-bit: Double (binary64)
- Can represent about 15 decimal digits of precision, enough to describe any position in the solar system with millimeter precision.
Extended precision
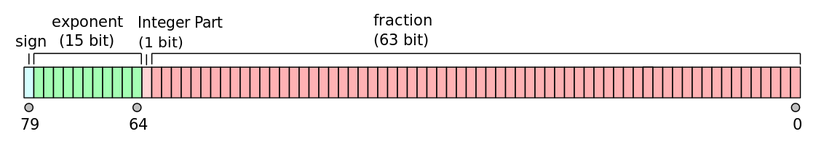
- The x86 extended precision format is an 80-bit format
long doubleinCis 80bits
128-bit: Quadruple (binary128)
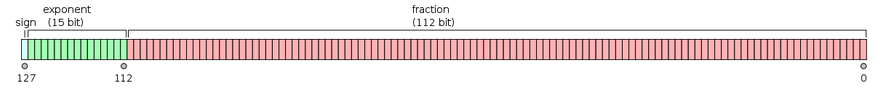
- This has no hardware support
__float128lacks hardware support, hence is slower than double.- Many space trajectory calculations use quadruple precision arithmetic, and most galactic evolution research considers statistical distributions rather than say something precise about the future state of the galaxy.
Arbitrary precision
- Arbitrary-precision arithmetic
- Implementations of much larger numeric types (w a storage count that usually is not a power of two) using special software
- The
dcandbcprograms are arbitrary precision calculators - Javascript uses arbitrary precision for
BigInt - IEEE754 does not require correctly rounded mathematical functions, it only recommends them. So, the accuracies vary from one mathematical library to another
When deciding what to use
For the same cost of doing a single float64 multiplication, you can do four float32 multiplications. So in practice, people choose the smallest data size that is good enough to work.
Floating Point and Processors
No FPU
What happens when certain precision is not supported by the CPU?
- The quad precision software floating point should speed up slightly, but it’s still implemented in scalar integer arithmetic.
x87 co-processor
Languages usage
Javascript
See Javascript JS has just 2 number types
number
Uses double-precision 64-bit binary format IEEE 754 or binary64.
- Safely represents between -(253 − 1) and 253 − 1 without loss of precision.
Number.MAX_VALUE: Largest number possible to representNumber.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER: Largest integer to be used safely in calculations.Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER: Smallest integer to be used safely in calculations.
BigInt
- Numeric primitive in JavaScript that can represent integers with arbitrary precision.
- Makes it possible to correctly perform integer arithmetic without overflowing.
Other notes
- One of the other things in I-triple-E 754 floating point numbers is an explicit encoding for things that are not numbers, like infinity.
Resources
Basics
- A brief introduction to interval arithmetic • Buttondown
- Fixed-point math is better than floating point (sometimes) - YouTube
- Float Exposed 🌟 (Also accompanied blogpost)
- Floating Point Numbers - YouTube
- Float Toy | Hacker News
- Floating Point Math 🌟 | Why does 0.1 + 0.2 = 0.30000000000000004?
- Fundamentals of Data Representation: Floating point numbers
- What Every Programmer Should Know About FP numbers
- Binary representation of the floating-point numbers | Trekhleb
- Floating Point Visually Explained
Wikipedia
Videos
- Representation of Floating Point Numbers - 1 - YouTube
- Numbers in a computer-(Unsigned Integers)-Part 1 of 5 - YouTube
Intermediate
- Examples of floating point problems 🌟
- Supporting half-precision floats is really annoying (2021) | Hacker News
- How many floating-point numbers are in the interval {0,1}? – Daniel Lemire’s …
- You can use floating-point numbers for money (evanjones.ca)
- Ordering Numbers, How Hard Can It Be? | orlp.net
- Formatting floating point numbers
Precision
- Half-Precision Floating-Point, Visualized / Ricky Reusser / Observable
- Demystifying Floating Point Precision « The blog at the bottom of the sea