tags : Floating Point, Concurrency, Flynn’s Taxonomy, Machine Learning
Learning resources
- Making Deep Learning go Brrrr From First Principles 🌟
- GPUs Go Brrr · Hazy Research
- Are GPUs For You
- We were wrong about GPUs | Hacker News
- GPU Programming: When, Why and How? — GPU programming: why, when and how? documentation
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3570638
- What Every Developer Should Know About GPU Computing
- What is a flop? | Hacker News
- Can we 10x Rust hashmap throughput? - by Win Wang
- 1. Introduction — parallel-thread-execution 8.1 documentation
- Udacity CS344: Intro to Parallel Programming | NVIDIA Developer
- AUB Spring 2021 El Hajj - YouTube
- How GPU Computing Works | GTC 2021 - YouTube
- Convolutions with cuDNN – Peter Goldsborough
- https://medium.com/@penberg/demystifying-gpus-for-cpu-centric-programmers-e24934a620f1
CUDA
The CUDA stack
| Level | Component Category | Key Components | Installation Status on Modal | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Kernel-mode driver | NVIDIA Accelerated Graphics Driver (e.g., 570.86.15) | Already installed | Tightly integrated with host OS; not user-modifiable. Communicates directly with GPU. |
| 1 | User-mode driver API | CUDA Driver API (libcuda.so), NVIDIA Management Library (libnvidia-ml.so), nvidia-smi CLI | Already installed on all Modal machines with GPU access | Allows user-space programs to interact with kernel drivers. nvidia-smi checks GPU status. |
| 2 | CUDA Toolkit | CUDA Runtime API (libcudart.so), Compiler (nvcc), nvrtc, cudnn, profilers, etc. | Not installed by default | Wraps CUDA Driver API. Tools for developing/debugging CUDA programs. |
Note on CUDA Toolkit Installation
- Not System-Wide by Default: Components of the CUDA Toolkit (like the CUDA Runtime API) are not pre-installed across the entire system on Modal.
- Python Package Dependencies: Many Python libraries (e.g.,
torch) bundle necessary CUDA Toolkit components (likenvidia-cuda-runtime-cu12) aspip-installable dependencies. This makes CUDA available to that specific Python application. - System-Level Requirement: Some tools or libraries require the CUDA Toolkit to be installed system-wide, not just within a Python environment. These tools may not find
pip-installed CUDA components. - Solution for System-Level: For applications needing a system-wide CUDA Toolkit, Modal recommends using official
nvidia/cudaDocker images, which come with the full toolkit pre-installed.
Resources
- Everything You Need To Know About CUDA Tensor Cores (98% util) - YouTube
- CUDA Programming Course – High-Performance Computing with GPUs - YouTube
- Course on CUDA Programming
- The CUDA Parallel Programming Model - 1. Concepts - Fang’s Notebook
FAQ
Different kinds of hardware for ML
| Feature | CPU | GPU | APU¹ | TPU | FPGA | ASIC² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General Compute | Graphics, Parallel | Combined CPU+GPU | ML Accelerate (NN/Tensor) | Reconfigurable Logic | Single Task Optimized |
| Architecture | Few Powerful Cores | Many Simple Cores | Mixed CPU/GPU Cores | Matrix/Tensor ASIC | Customizable Logic Grid | Custom Fixed Hardware |
| ML Since | Always | 2000s (GPGPU), 2012 | 2010s (Integrated) | 2015 (Internal), 2018 | Mid-2010s (Accel.) | Mid/Late 2010s (ML) |
| ML Prevalence | System Base, Light ML | Very High (Training) | Moderate (Edge/PC) | Growing (Google Cloud) | Niche (Low Latency) | Growing Fast (Infer.) |
| ML Advant. | Flexible, Sequential | Parallelism, Ecosystem | Balanced, Power/Cost Eff | Perf/Watt (Matrix), Scale | Customizable, Low Latency | Max Perf/Watt (Task) |
| ML Limits | Poor Parallel | Power, Sparse Data | Shared Resource Limits | Less Flexible, Ecosystem | Complex Dev, HW Skill | Inflexible, High NRE |
| ML Use Cases | Data Prep, Orchestrate | DL Training, Inference | Edge AI, Mixed Loads | Large Scale DL (GCP) | Real-time Inference | High-Vol Inference |
Nvdia GPUs
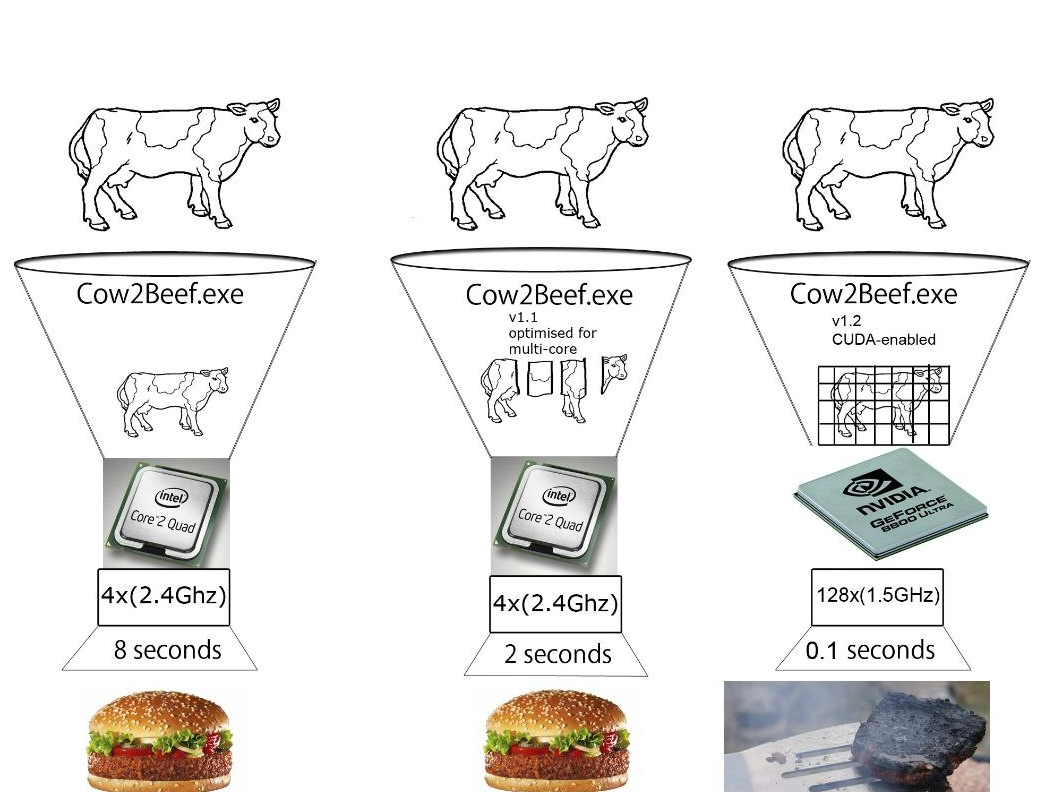
CUDA core
- CUDA cores each core can only do one multiply-accumulate(MAC) on 2 FP32 values
- eg. x += x*y
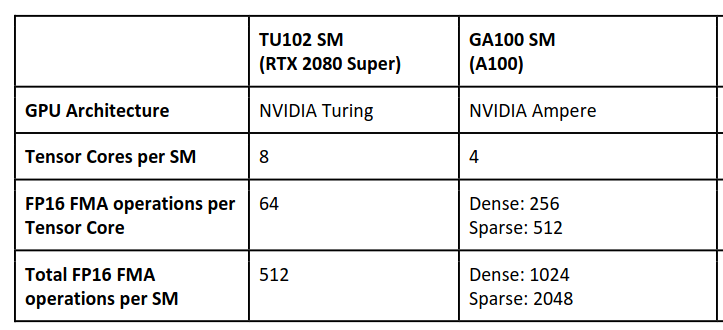
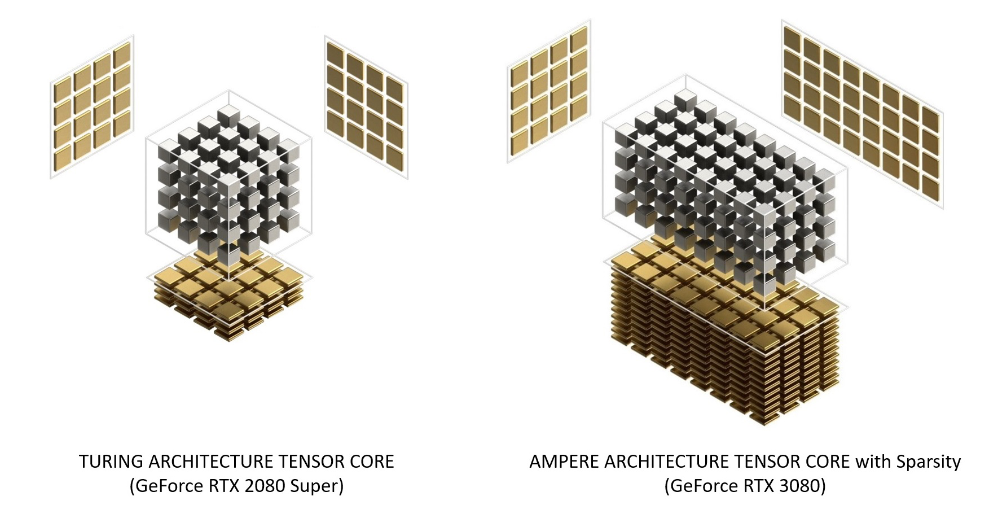
Tensor core
- Tensor core can take a
4x4 FP16matrix and multiply it by another4x4 FP16matrix then add either aFP16/FP32 4x4matrix to the resulting product and return it as a new matrix.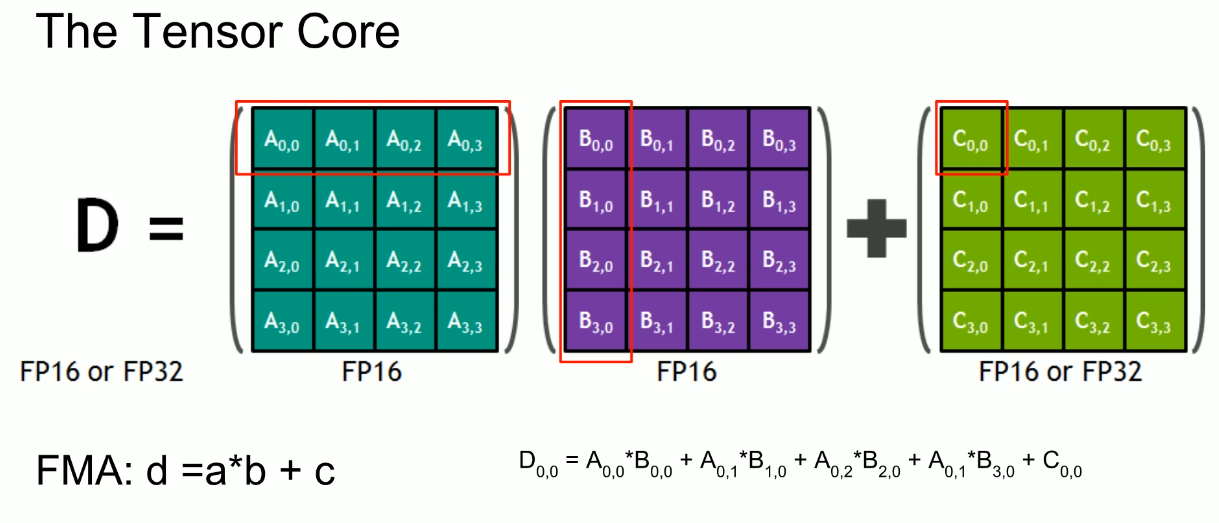
- Certain Tensor cores added support for
INT8andINT4precision modes for quantization.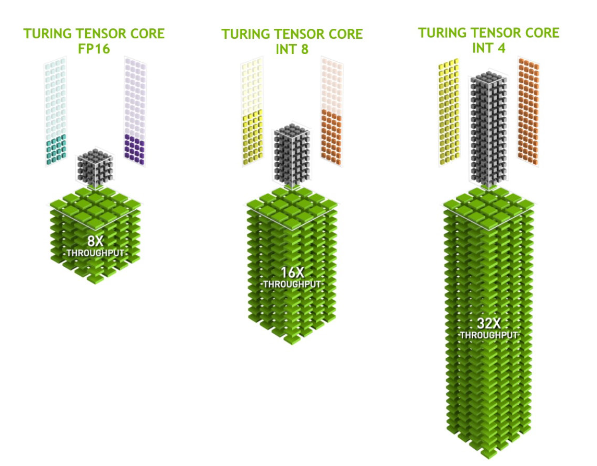
- Now there are various architecture variants that Nvdia build upon, Like Turing Tensor, Ampere Tensor etc.
 See Category:Nvidia microarchitectures - Wikipedia
See Category:Nvidia microarchitectures - Wikipedia
RAM
???
VRAM
- Memory = how big the model is allowed to be
Related topics
Performance
- Typically measured in floating point operations per second or
FLOPS/GFLOPS - Good if the no. of floating point operations per memory access is high
Floating Point support
See Floating Point
- GPUs support
half,singleanddoubleprecisions doubleprecision support on GPUs is fairly recent.- GPU vendors have their own things and support
F32
float32 is very widely used in gaming.
- float32 multiplication is really a 24-bit multiplication, which is about 1/2 the cost of a 32-bit multiplication. So an int32 multiplication is about 2x as expensive as a float32 multiplication.
- On modern desktop GPUs, the difference in performance (FLOPS) between float32 and float64 is close to 4x
Frameworks
- OpenCL: Dominant open GPGPU computing language
- OpenAI Titron: Language and compiler for parallel programming
- CUDA: Dominant proprietary framework
More on CUDA
- Graphic cards support upto certain cuda version. Eg. my card when
nvidia-smiis run shows CUDA 12.1, it doesn’t mean cuda is installed - So I can install cudatoolkit around that version.
- But cudatoolkit is separate from nvdia driver. You can possibly run cudatoolkit for your graphic card without having the driver.
-
Pytorch
- Eg. To run Pytorch you don’t need cudatoolkit because they ship their own CUDA runtime and math libs.
- Local CUDA toolkit will be used if we build PyTorch from source etc.
- If pytorch-cuda is built w cuda11.7, you need cuda11.7 installed in your machine. Does it not ship the runtime????
nvccis the cuda compiler- torhaudio: https://pytorch.org/audio/main/installation.html
-
Setting up CUDA on NixOS
- So installing nvidia drivers is different game. Which has nothing to do with cuda. Figure that shit out first, that should go in configuration.nix or whatever configures the system.
- Now for the CUDA runtime, there are few knobs. But most importantly LD_LIBRARY_PATH should not be set globally. See this: Problems with rmagik / glibc: `GLIBCXX_3.4.32’ not found - #7 by rgoulter - Help - NixOS Discourse
- So install all CUDA stuff in a flake, and we should be good.
- Check versions
nvidia-smiwill give the cuda driver version- After installing
pkgs.cudaPackages.cudatoolkityou’ll havenvccin your path.- Running
nvcc --versionwill give local cuda version
- Running
- For flake
postShellHook = '' #export LD_DEBUG=libs; # debugging export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="${pkgs.lib.makeLibraryPath [ pkgs.stdenv.cc.cc # pkgs.libGL # pkgs.glib # pkgs.zlib # NOTE: for why we need to set it to "/run/opengl-driver", check following: # - This is primarily to get libcuda.so which is part of the # nvidia kernel driver installation and not part of # cudatoolkit # - https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/issues/272221 # - https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/issues/217780 # NOTE: Instead of using /run/opengl-driver we could do # pkgs.linuxPackages.nvidia_x11 but that'd get another # version of libcuda.so which is not compatiable with the # original driver, so we need to refer to the stuff # directly installed on the OS "/run/opengl-driver" # "${pkgs.cudaPackages.cudatoolkit}" "${pkgs.cudaPackages.cudnn}" ]}" ''; - Other packages
- sometimes we need to add these to LD_LIBRARY_PATH directly
pkgs.cudaPackages.cudatoolkitpkgs.cudaPackages.cudnnpkgs.cudaPackages.libcublaspkgs.cudaPackages.cuda_cudartpkgscudaPackages.cutensor