tags : Computer Architecture, Operating Systems, Concurrency
VAS for different architectures
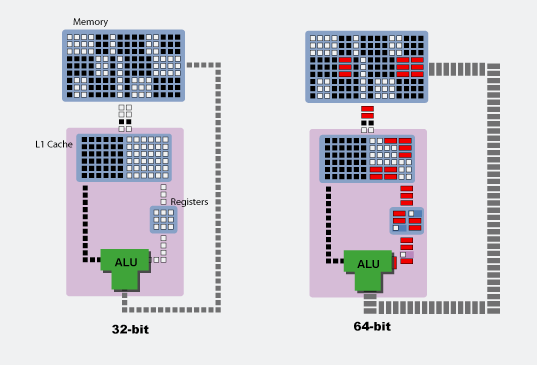
32/64/48address space, each bit can be1or0, hence . See Permutations & Combinations.- IA-32/x86_32/x86/i386
- ~= 4GB (32 bit address size)
- 32 bit machines can still support more ram.(PAE)
- x86_64/amd64
- ~= 18EB (64 bit addresses)
- 2^{48}^{} ~= 16EB (48 bit addresses)
- For our use tho, we get only 128TB. Which is not “only” tbf.
- Why do x86-64 systems have only a 48 bit virtual address space?
- https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/x86/x86_64/mm.txt
vCPUs
You always have at least one core, one die and one package.
| Name | What |
|---|---|
| Package | What you get when you buy a single processor. Contains one or more dies. |
| Die | Actual silicon. A die can contain any number of cores |
| Socket | The physical connector linking the processor to the computer’s motherboard. There can be multiple. |
| Core | Independent execution unit that can run one program thread at a time in parallel with other cores. |
| vCPU | vCPUs are compute threads that process execution for running os/vm. |
vCPU calculation
(# Sockets)*(# Cores)=(# pCPU)(Physical CPU)(# pCPU)*(2 Threads)=(# vCPU)(Virtual CPU)
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 4
Socket(s): 1
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7 (8)
pCPU = 1 * 4 = 4
vCPU = 4*2 = 8VMs and Hypervisors
Now the term vCPU is widely used in hypervisors etc. In those cases, most hypervisors will let you overprovision cores. That means, you could assign 1 vCPU per VM, but the hypervisors also allow you overcommit every vcpu if you think your workload could handle that.
x86 Microarchitecture levels (march)
- See x86-64 - Wikipedia
- See x86 Options (Using the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC))
- See x86-64 Microarchitecture Feature Levels
- uops.info
- We can tell compilers about available instruction-set to optimize for using
marchflag - These features have to be supported by the CPU in the first place. You can search for your CPU at CPU-World and see supported features.
- Enabled features can be found at
cat /proc/cpuinfo - You can check supported levels with
/lib/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 --helpx86-64-v4 x86-64-v3 (supported, searched) x86-64-v2 (supported, searched) - The v2-v4 levels are arbitrary names defined by grouping different instruction sets based on their age and usefulness.
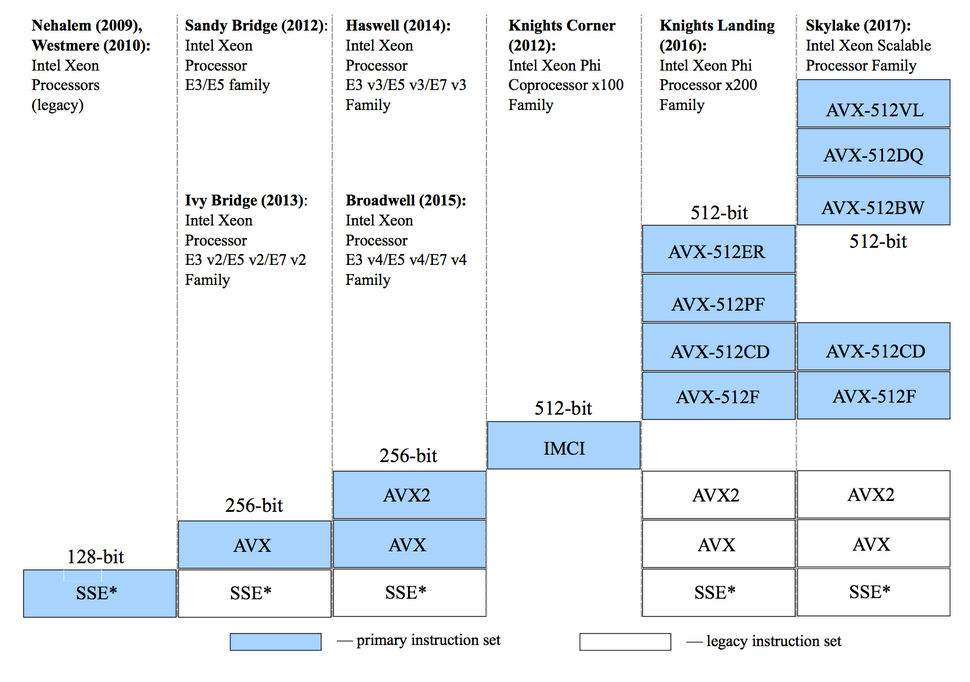
x86-64-baseline
- CMOV, CMPXCHG8B, FPU, FXSR, MMX, FXSR, SCE, SSE, SSE2
x86-64-v2
- CMPXCHG16B, LAHF-SAHF, POPCNT, SSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSSE3
- close to Nehalem
- Basically mandatory for modern OS
x86-64-v3
- AVX, AVX2, BMI1, BMI2, F16C, FMA, LZCNT, MOVBE, XSAVE
- close to Haswell
- Nice to haves
x86-64-v4
- AVX512F, AVX512BW, AVX512CD, AVX512DQ, AVX512VL
- Cutting edge enterprise feature sets
Word
- See wordsize w
$ getconf WORD_BITandLONG_BIT(32on my computer) - WORD (16 bits/2 bytes)
- DWORD (32 bits/4 bytes)
- QWORD (64 bits/8 bytes)
Registers
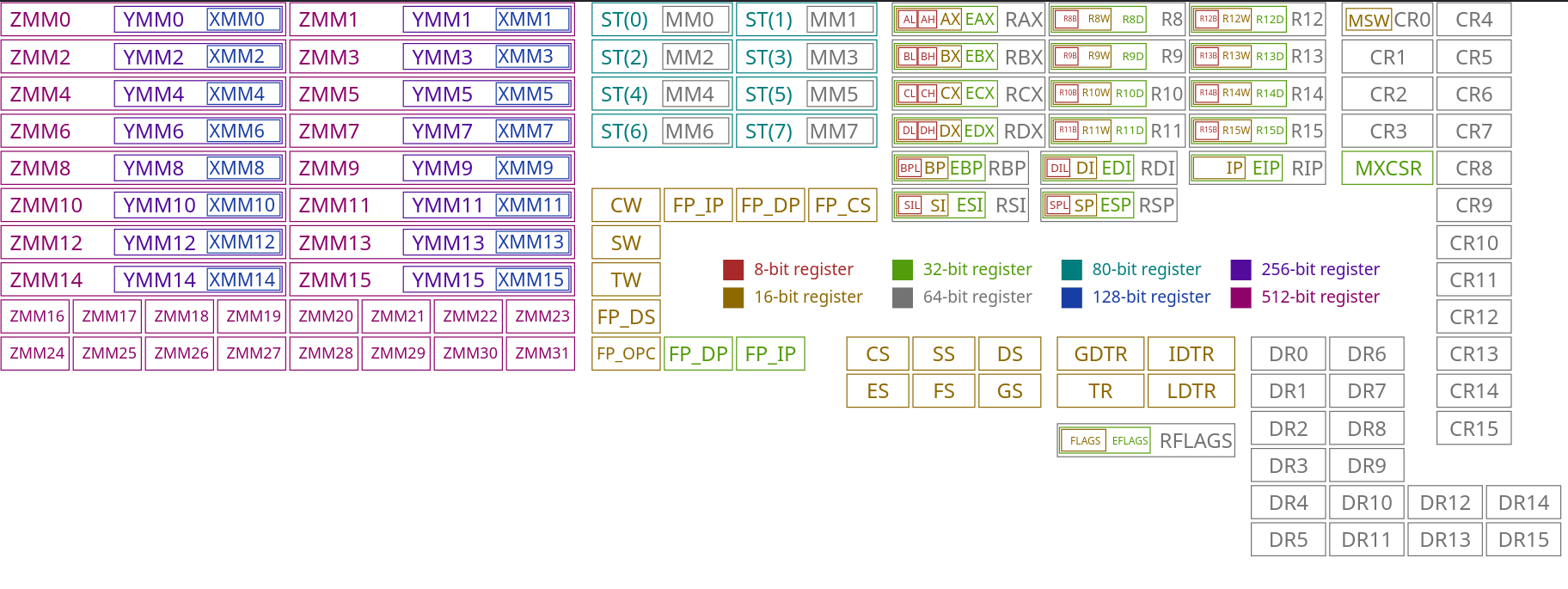
Glossary
Chipset
- Thing that’s in the motherboard that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. i.e I/O Bridge.