tags : Cryptography, Security, PKI, HMAC
Cipher
These in the vanilla form use symmetric keys
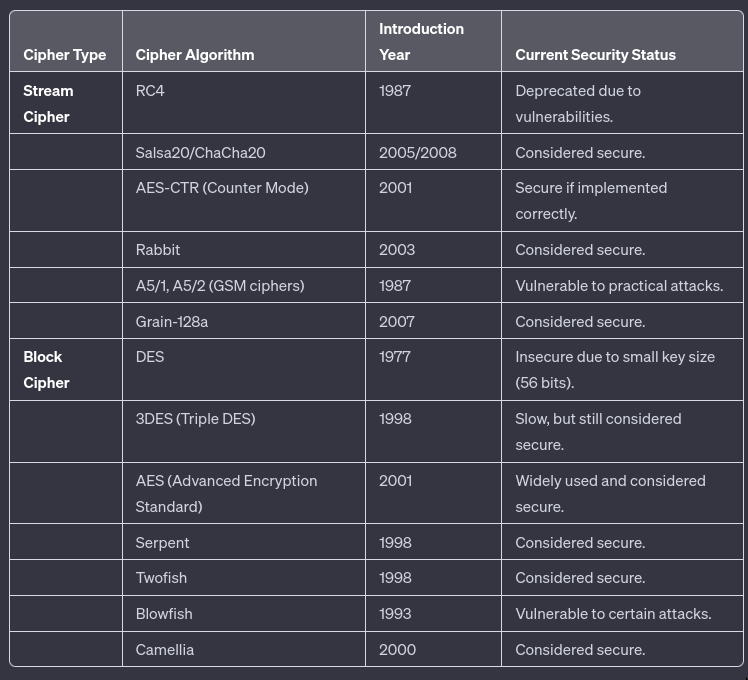
Block Cipher
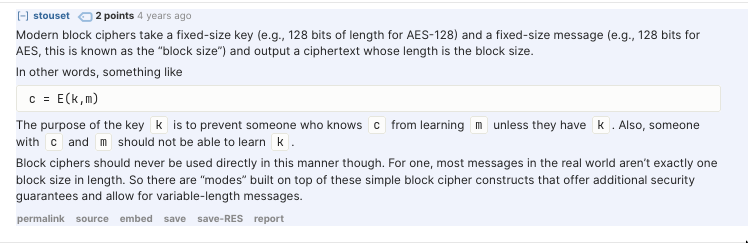
fixed-size key x fixed-size message = ecncryted message of block size- The different “modes” help operate block cipher
- A secure “random-looking id generator”
- Block ciphers with less than 128 bits of output are widely considered insecure: this corresponds to about 22 base64 characters.
- A block cipher is an algorithm that encrypts blocks of a fixed length. The encryption function E transforms plaintext blocks P into ciphertext blocks C by using a secret key k.
Stream Cipher
- A stream cipher is a
symmetric-key encryptionalgorithm that encrypts a stream of bits. - Ideally, that stream could be as long as weʼd like; real-world stream ciphers have limits, but sufficient for practical use
Stream vs Block
- Several block ciphers have modes of operation that allow them to function in a streaming-like manner.
- Cipher Feedback (CFB)
- Output Feedback (OFB)
- Counter (CTR) etc.
- With stream ciphers, we know(after encryption has happened) that certain metadata is at certain indices in the stream.
What do I know about the plaintextandwhat can I LEARN about the plaintext from observing the ciphertextare two different things.- This is a “priori knowledge”. The fact that you used a stream cipher didn’t change anything, but it also didn’t leak anything.
- Stream cipher may seem less secure compared to a block cipher (In a block bits are sort of jumbled around & don’t have fixed position)
- But if we ensure
authenticity,integrity(HMAC), we’re good. With stream cipher the attacker can know what could be where based on the protocol but does not know nothing about the actual data. So we all good.
TODO MODES
block
-
Electronic Codebook (ECB):
- Each block of plaintext is independently encrypted with the same key.
- Identical plaintext blocks result in identical ciphertext blocks.
-
Cipher Block Chaining (CBC):
- Each plaintext block is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before encryption.
- Initialization Vector (IV) is used for the first block to break patterns.
-
Cipher Feedback (CFB):
- Turns a block cipher into a stream cipher.
- Previous ciphertext block is fed back into the block cipher to generate a keystream.
-
Output Feedback (OFB):
- Similar to CFB but the block cipher encrypts a constant value (IV) to produce a keystream.
- The keystream is then XORed with the plaintext.
-
Counter (CTR):
- Turns a block cipher into a stream cipher.
- Uses a counter as the input to the block cipher to generate a keystream.
- The counter is usually combined with a nonce.
-
Galois/Counter Mode (GCM):
- Combines the counter mode of operation with Galois field multiplication.
- Provides both confidentiality and authenticity.
- Widely used for authenticated encryption.
Stream Cipher Modes:
- Synchronous Stream Ciphers:
- Keyed bits are generated to form a pseudorandom keystream.
- The keystream is then XORed with the plaintext to produce the ciphertext.
- Self-Synchronizing Stream Ciphers:
- Previous ciphertext bits are used to generate the next key bits.
- Allows synchronization even if some ciphertext bits are lost or corrupted.
- Stream Cipher with Feedback (SCFB):
- Similar to CFB mode for block ciphers.
- Uses the previous ciphertext bits to generate the next keystream.
- Combining Generators:
- Multiple keystream generators are combined to improve security.
- Filter Generators:
- Combines a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) with a nonlinear filter.
Encryption in Practice
Encryption itself is vulnerable to tampering unless you combine it with authentication. Hence AEAD.
Backup and data recovery
More info Could Age Replace OpenPGP? {The Call of the Open Sidewalk}
Bad data
- Different encryption tools like GPG and
agemay deal with this differently. - So good to check the integrity of the input file before attempting to do anything with it.
- Example
age: No data or partial data is better than bad data$ age -d -i key.txt -o totc_out.txt totc.txt.age Error: chacha20poly1305: message authentication failed [ Did age not do what you expected? Could an error be more useful? Tell us: https://filippo.io/age/report ] $ ls -l totc_out.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 operator operator 0 Dec 25 12:53 totc_out.txt # zero length output!! - Example
gpg: Partial bad data is better than no data$ gpg2 -d totc.txt.pgp >totc_out.txt gpg: encrypted with 2048-bit RSA key, ID B456C3BB5A48A0EA, created 2020-06-01 "BACKUP <backup@store>" gpg: WARNING: encrypted message has been manipulated! $ ls -l totc_out.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 operator operator 807615 Dec 25 15:26 totc_out.txt
Database data encryption
- The laziest solution to the “encrypted database” use-case is to just use deterministic encryption, such as AES-ECB or with a static IV/nonce. (NOT GOOD)
- DO: Encrypt securely (i.e. AEAD with random nonces).
AEAD (Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data)
encryption scheme that ensures both confidentiality and authenticity of the data. + allows you to associate extra authenticated but un-encrypted data.
- It’s a construction
- Main idea is: Encrypt-then-MAC
- But by using combined algorithms such as
ChaCha20-Poly1305, it makes the “Encrypt-then-MAC” step into one and makes things easier for us.
- Components
- Encryption: Symmetric key (Eg. AES,
ChaCha20) - Authentication: HMAC or
Poly1305 - Extra associated data
- Encryption: Symmetric key (Eg. AES,