tags : Linux
Important Resources
- ChromiumOS Docs - Linux System Call Table
- The Definitive Guide to Linux System Calls | Packagecloud Blog
ausyscall --dump: List syscalls in the system- UNIX Syscalls
Other resources
Kernel and CPU
- This happens via Interrupts
- What are the calling conventions for UNIX & Linux system calls
- How syscalls work in rust
Kernel and Userland
Entry points into the kernel
- syscalls
- exceptions
- traps
Notifications from kernel to userland process
- Error codes from syscalls
- Signals: software interrupts sent by the kernel to a specific process to notify it of an event.
- File Descriptors: Using something like
eventfdand then usingpoll/select/epoll - FS based notification: Eg. inotify
Directory
Memory
brk/sbrk
We have a syscall to do this, brk and sbrk (wrapper around brk that allows a increment rather than direct address unlike brk), when we are using brk it gives us new memory based on the page size(see obj header diagram above)
mmap
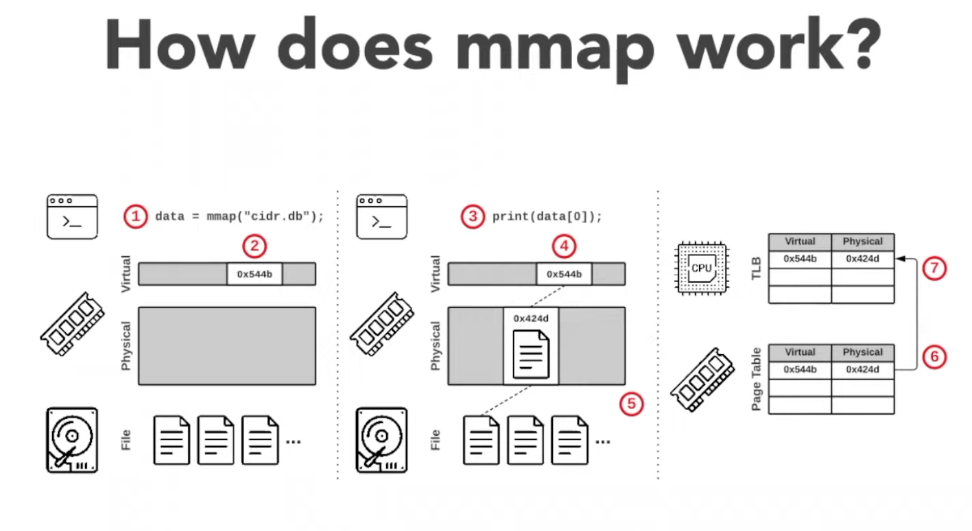
- See mmap
mlock
- When
mlockis set, it won’t flush that portion into swap. - Misunderstanding mlock(2) and mlockall(2)
-
What it for?
- programs that need to store passwords or sensitive decrypted data in memory (See Vault and mlock() – HashiCorp Help Center)
- programs that need to operate in a real-time environment
-
What it not for but used for
- Increasing performance by letting things not go to swap. In these cases you might aswell just disable swap for that program(cgroups) rather than setting mlock.
- Some systems still will swap even if you set mlock
io
ioctl
- When an application interacts with a driver, it can use
read,writebut it can also useioctlto send specific stuff.
Process
clone
cloneallows you to explicitly specify which parts of the new process are copied into the new process, and which parts are shared between the two processes.- Using certain flags, we can either create
threadsorprocessesusingclone() thread: Everything is copied except memory. (Memory is shared). See Threads and Thread Safety
fork
- A call to
fork()is equivalent to a call toclone(2)specifying certain flags. (CLONE_VM) - Not used to create Threads but Processes
- It creates a copy of itself
- It creates a child
processwhose page table is a clone of the parent using CoW. i.e Memory is copied, not shared.
exec
- When we
fork(), page table is copied to the child w Copy on Write semantics. - When we
exec(), it blanks the process’s current page table, discarding all existing mappings, and replaces them with a fresh page table containing a small number of new mappings- An executable
mmap()of the new file passed to theexec()call. - env vars and command line arguments, same pid, a new process stack, and so on.
- An executable
- That’s why to launch a new process in Unix-like systems, we do
fork(), followed immediately by a call toexec()(execve())
setenv
Advice
These are only acting advisory. The kernel is not obligated to follow them.
fadvice
- provide hints to the operating system about the application’s file access patterns.
- Sequential, Random, will need etc.
madvice
- provide hints to the operating system about the usage pattern of memory mapped by a process.
- Sequential, Random, will need etc.