tags : Memory Hierarchy, Virtual Memory, O, Copy on Write, Computer Bus
FAQ
What basic things to know?
- Not all physical memory addresses are “DMA-able”.
- Userspace can’t DMA atm. Security issues.
- Not all devices support DMA
IS DMA a security issue?
- Yes, a security problem in a way
- IOMMU provides protection by giving permissions to devices on what memory address spaces they can access.
What?
- An overview of direct memory access | The Infinite Loop
- DMA means devices can access physical memory independently of the CPU
- DMA is rather a concept than a specific technology. There is no specification which describes in detail how DMA transfers work.
Uses
- Typical application is communicating with peripheral devices plugged into a bus system like ATA, SATA, PCI or PCI Express. (the one we care about atm)
- intra-core communication in micro processors
- Copy data from the memory of one computer into the memory of another computer over the network via remote DMA
Implementation
Third party DMA using ISA
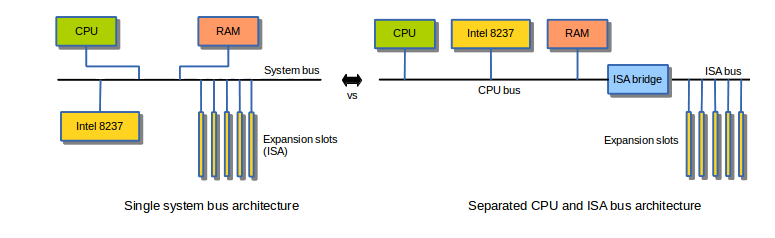
- Bus topology
- These used DMA controller
- The DMA controller could be programmed by the CPU to perform a number of memory transfers on behalf of the CPU. This way of accomplishing DMA transfers is also known as third party DMA.
PCI DMA
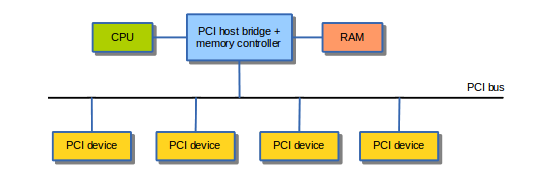
- Introduced bus mustering. No more DMA controllers.
- i.e only one device at a time to access the bus.
- The CPU, the DMA controller and bus masters could all be competing for memory access. The memory arbiter typically favors the CPU
- Compared to DMA controller, with bus mustering devices must contain a
DMA enginedriving the memory transfers.
PCIe DMA
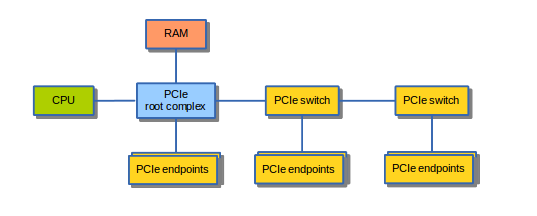
- Star topology, Point-to-Point/Serial.
- Arbitration by the “root complex”
- PCIe supports full duplex DMA transfers of multiple devices at the same time.