tags : Machine Learning, Statistics
FAQ
“correlation does not implies causation” meme
- “correlation does not implies causation” : Yes, commonly said
- But causation also does not imply correlation too. There can be hidden variables.
What are associations?
correlationis a limited measure ofassociationvariablescan beassociatedbut have nocorrelation
associationare bi-directional:associationsbetweenvariablesrun in both direction
Basics
What is Causal Interference
- What happens when some intervention is done
- Can only be done if we have a causal model
Causal Prediction
- Different from normal prediction
- Predicting the effect
- Being able to
predict the consequencesof anintervention. - Eg.
Movement of the treesandwindare staticallyassociated. But nothing in the data tells you thatwindcauses the trees to move.
- Being able to
- What if I do this?
Causal Imputation
- Knowing the cause
- Being able to
constructsomeunobserved counterfactual outcome
- Being able to
- What if I had done something else?
Related topics to Causal Inference
- Description (of
population)- The
sampleiscausedbythings
- The
- Design (of research project)
thingsneed to be drawn w a causal logic which will help usdesign/calculatearound them- thinking about why
samplediffers from thepopulation
Models
DAGs
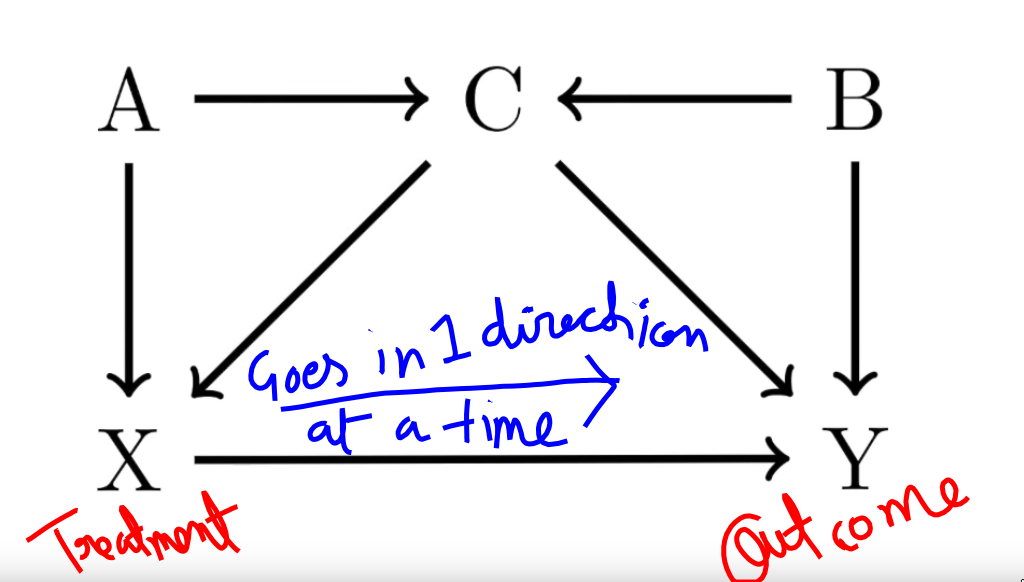
- Example
- Here
Ainfluences the treatmentX - Here
Binfluences the outcomeY - Here
Cinfluences bothXandY(Confound, we’d want to control it)
- Here
- We can ask multiple questions to this model
- DAGs are intuition pumps: get head out of data, into science
- Gives you a strategy for which
control variablesyou need to play with
GOLEMS
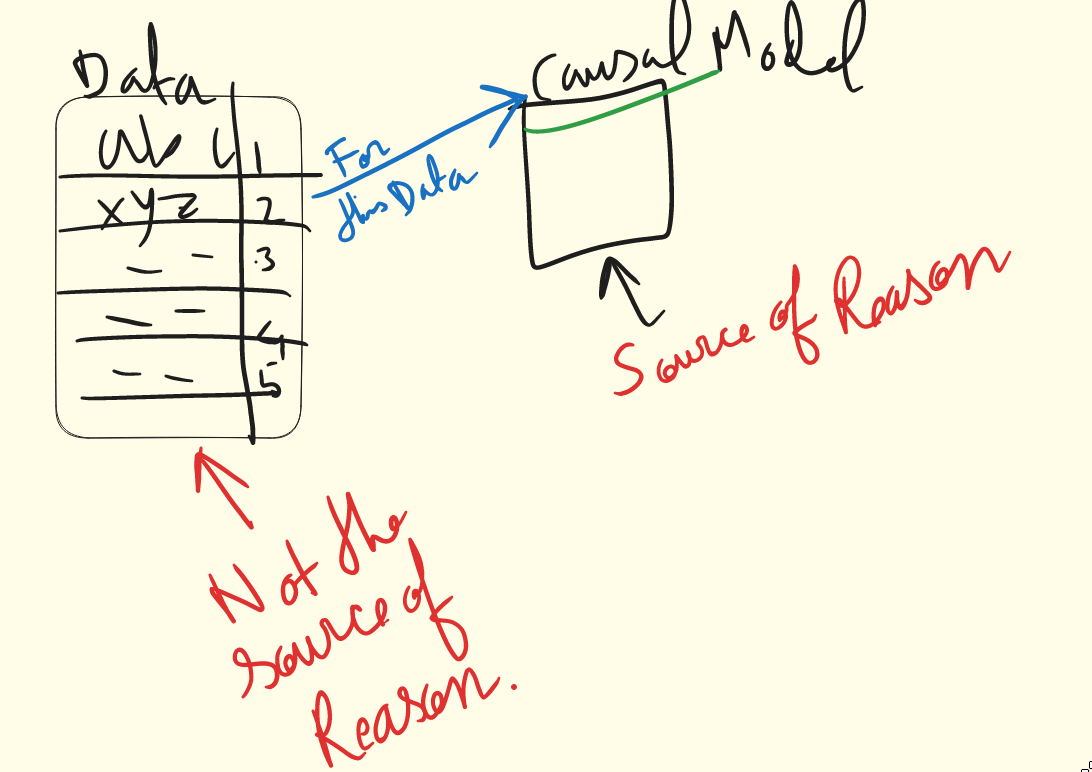 statistical models to produce scientific insight
statistical models to produce scientific insight
- They require additional
scientific (causal) models - The
reasonsare not found in the data, but rather in thecausesof the data- i.e We should not try to infer the reason in the data.
No causes in(the data), No causes out(from the data)
Decision Tree/Flowchart
- We use it for selecting an appropriate statistical procedure.
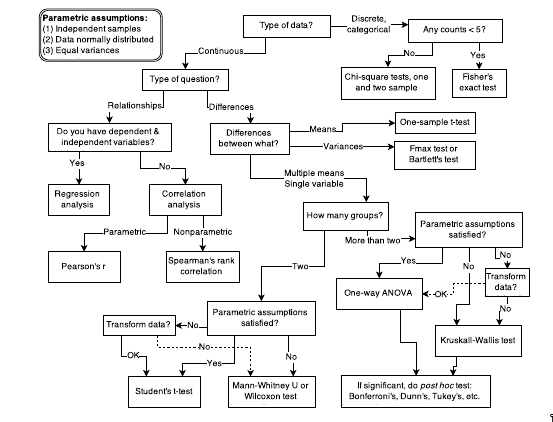
- But this kind of using a decision tree to select the statistical procedure is not much helpful for a research scientist because this quite limiting
- Each of these procedures can have bayesian and frequestist version of them
- Mostly useful in industrial testing