tags : Message Passing, Design Patterns
FAQ
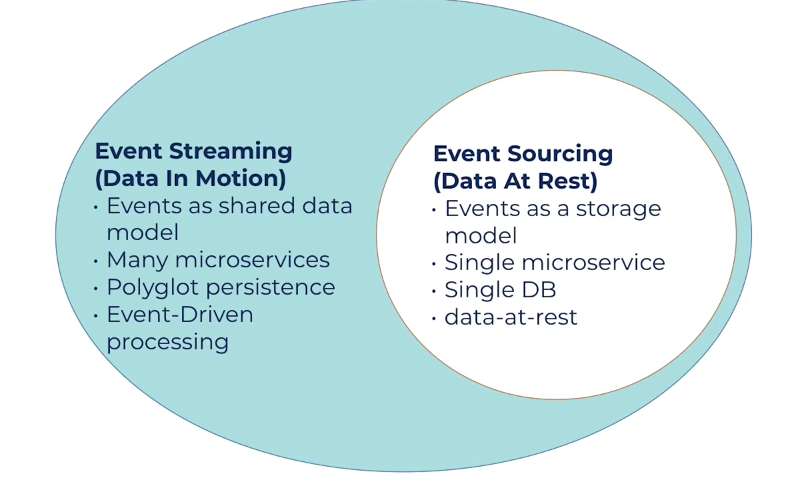
Streaming vs Processing
These terms are vague, on top of that redpands, pulsar etc. mix these together
Event streaming:Storageandmovementof data in real timeEvent processing:Processingandconnectivityof data. connecting source & destination.- Eg. kafka ecosystem
Storage and movement: Kafka brokerConnectivity: kafka connect, flink also can doProcessing: ksqldb, flink, kstream
Message based vs Event driven
Distributed systems often require data and system updates to happen as quickly as possible. In software architecture, these updates can be handled with either messages or events.
- With messages, updates are sent directly from one component to another to trigger an action.
- With events, updates indicate that an action occurred at a specific time, and are not directed to a specific recipient.
An event is simply a record of something changing state. For example, the event of a credit card transaction includes the product purchased, the payment, the delivery, and the time of the purchase. The event occurred in the purchasing component, but it also impacted the inventory, the payment processing, and the shipping components.
What Models
Model to think about data at rest and data in motion about real world systems.
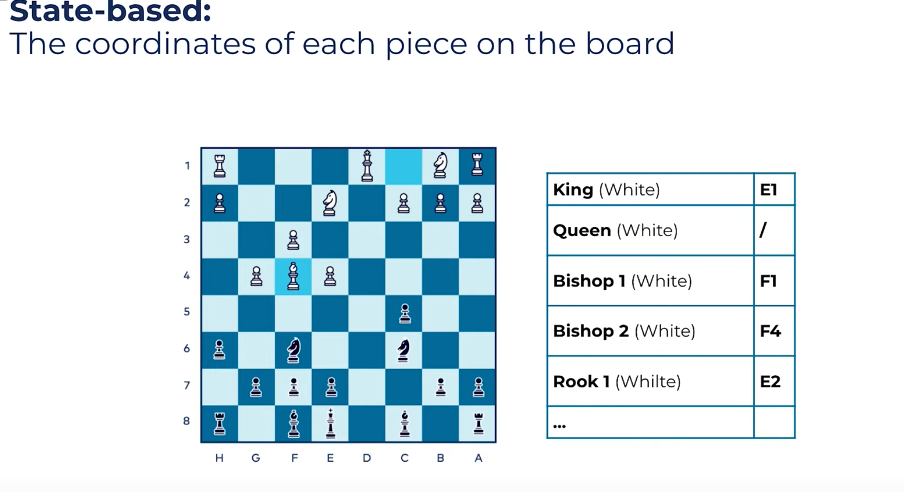
State based
- Source of truth: A table that can be mutated
- This is the more traditional model.
- More live a snapshot in time
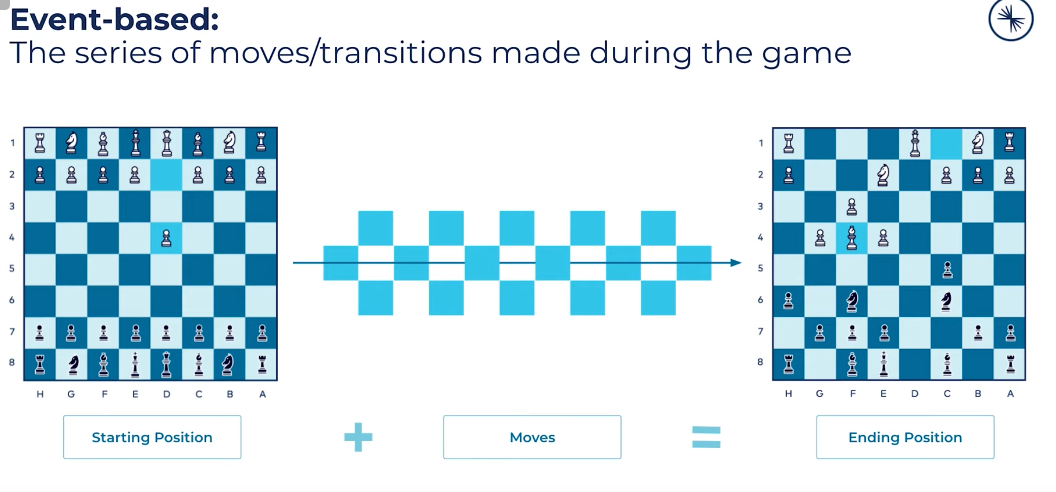
Events based

-
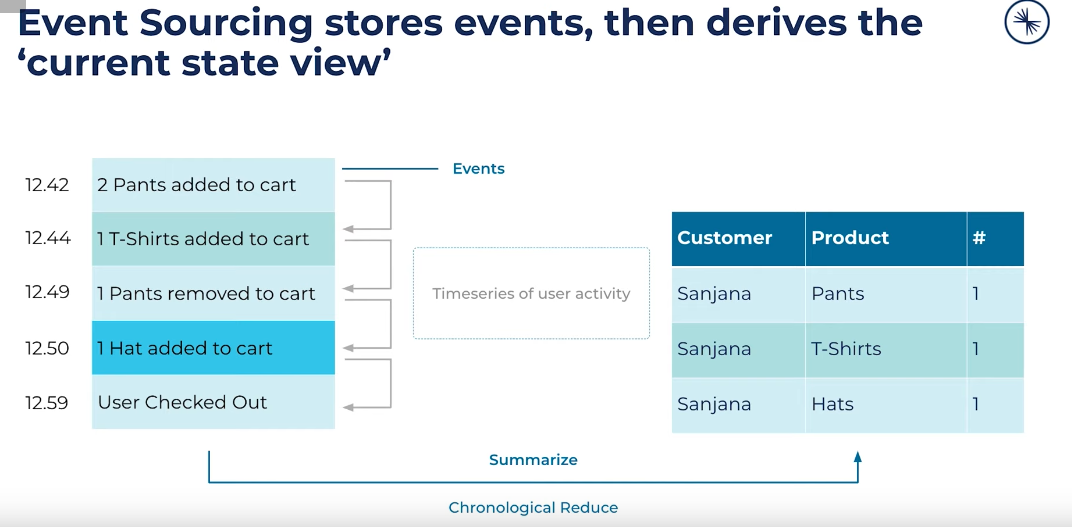
Source of truth: Event log
-
Storing your data as events
-
Retains more data than state based system
-
Events are immutable (You can’t change the past)
-
Event sourcing, Event Streaming, CQRS etc.
-
Current view
- Whole stream of events is required to derive the current position
Advantage
- Immutability
- Recoverability: If we discover a bug in our system, once we fix the bug, fixing the data is simply replaying the event stream from that previous point.
Disadvantage
- Event log can now contain many different versions of the same schema
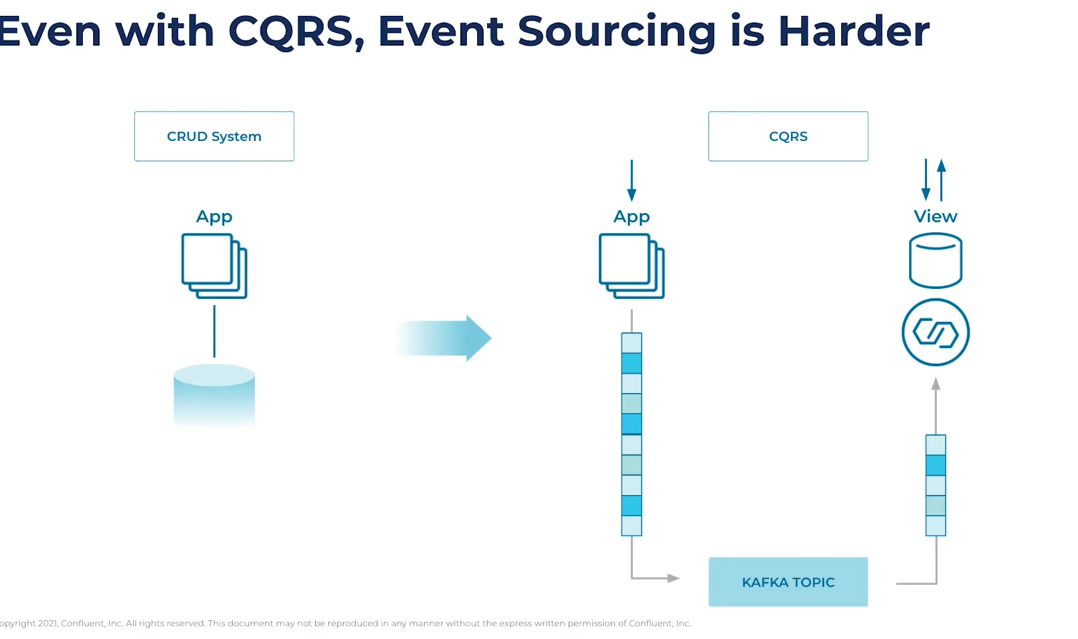
Event Sourcing w CQRS
- Command Query Responsibility Segregation
- At its heart is the notion that you can use a different model to update information than the model you use to read information.
- CQRS is not the only way to do this, but most probably one of the most common ways
Writing
We write to append only log as events happen
Reading / CQRS
-
Usually to read from a event log, you’ll need to do a chronological reduce over the data. This can take a lot of time based on the size of the data.
-
Solution is to compute this at write time(async).
-
Because of this, system becomes Eventually consistent 🌟
- Reads might not be immediately available after write.
CDC
See CDC ( Change Data Capture )
Event Streaming