tags : Data Engineering
FAQ
How does Delta table related to batch/stream processing
Every table in a Delta Lake is a batch and streaming sink.
What’s the Consistency Model ?
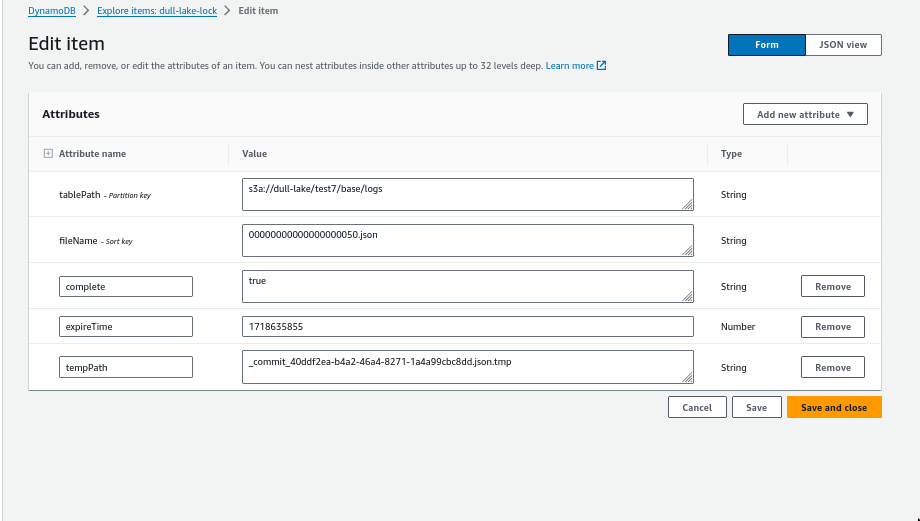
- Serializable
- Basically acquire a shared singular lock on the table.
- The Delta Lake protocol expressly relies on “atomic primitives of the underlying filesystem to ensure concurrent writers do not overwrite each others entries.”
- Understanding Delta Lake’s consistency model — Jack Vanlightly
- Concurrency limitations for Delta Lake on AWS
- Transactions - Delta Lake Documentation
s3 x dynamodb- we need dynamodb for managing the locking logic, but individual delta tables don’t need individual dynamodb. i.e one dynamodb table is enough for multiple buckets/multiple delta tables.
- Keys are: range_key=“fileName” and hash_key=“tablePath”
Delta Lake and Streaming
- Some people are using it as a https://github.com/delta-io/delta-rs/issues/413
- Delta lake supports streaming but delta-rs package has some limitations I think
How delta-rs and pyarrow and polars are related?
Delta-rs can read a delta table and create a pyarrow table in memory, which you can then use to create a polars dataframe.
Benifits of delta table over plain parquet
- Schema evolution
- Versioning
- Delta tables always return the most up-to-date information, so there is no need to call REFRESH TABLE manually after changes.
- See if we have this gurantee with
delta-rs
- See if we have this gurantee with
Partitioning on a column in which we change values!
Delta Table/Lake usage
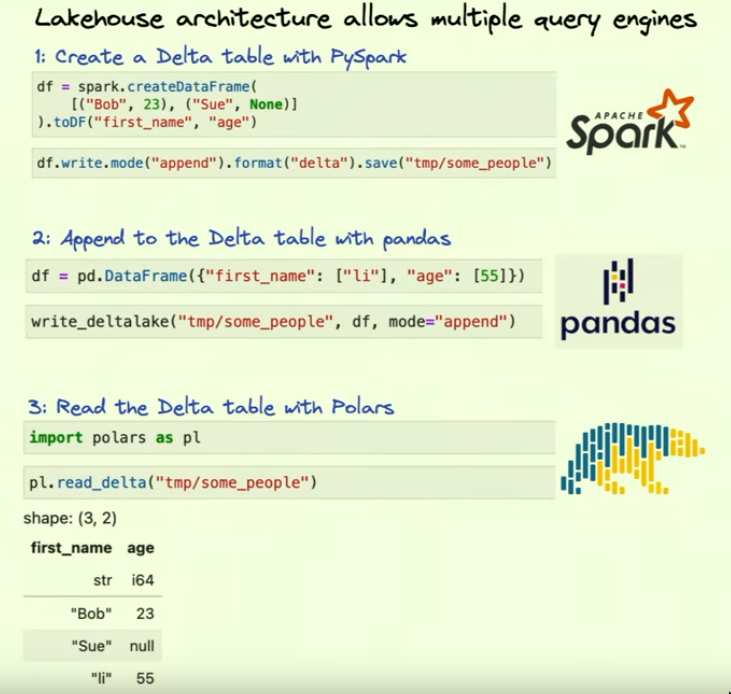
- Earlier this was only available to be used via Spark based APIs. But with
delta-rs, this changes and we can access delta lake with other APIs. - DuckDB with pyarrow
- Uses
delta-rs, an of the Delta Lake protocol in Rust, featuring Python bindings.
- Uses
- Polars
- Polars Delta Lake connector depends on
delta-rs
- Polars Delta Lake connector depends on
- Kafka
Operations in Delta Lake / Table
- These are differently named in
delta-rslib and original delta lake terminologies- Thing is not worry about how things are looking in the delta table repository, there can be multiple versions etc. appends can keep older files, etc. compaction will compact files etc. Just thinking in terms of operations is good enough. Ideally, you never want to touch the delta table directory manually.
- Some delta.io documentations use
delta-sparkpython package. We are using the deltalake python package which is part of the delta-rs project. delta-rsis a delta lake implementation in rust on top of pyarrow, which does not need spark. Great for small scale pipelines!- Finally we might want to use
polarsbecause it builds on top ofdelta-rsand gives us nice wrappers in which we don’t need to deal with pyarrow direrctly and has helper methods and optimizations. - Some delta documentations have mentions of
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETEandMERGE. which can be applied to a table. - All operations on delta table are logical., i.e if you delete, it’s not really deleted etc.
vaccummis later used to actually remove files from disk.- TODO: What about merge??
Writer methods
- We’re following what
delta-rswrite gives us:‘error’, ‘append’, ‘overwrite’, ‘ignore’ - Additionally if we use polars, we can use
mergealong with this. But usingmergeneeds us to do additional things. If we’re not using polars, we need to do merge by getting the pyarrow thing manually.
error
append
- There is no way to enforce delta table column to have unique values. So we want to use append only if we can ensure that there are no duplicates.
- If you don’t have Delta table yet, then it will be created when you’re using the append mode.
- Mode “append” atomically adds new data to an existing Delta table and “overwrite” atomically replaces all of the data in a table.
-
Merging vs Append
- Append: When you know there are no duplicates
overwrite
- Instead of writing data in the append mode, you can overwrite the existing data. But this still will duplicate files in storage
ignore
merge
- You have some JOIN between one or more columns between two Delta tables. If there is a match then UPDATE, otherwise if there is NO match then INSERT.
- There can be multiple
whenMatchedandwhenNotMatchedclauses
-
Concerns
- A merge operation can fail if
multiple rows of the source match the targetand then we try to update target table. - Merge in delta table requires 2 pass over the source dataset, so
mergecan produce incorrect results if the source dataset is non-deterministic(eg. current time).- Eg. Reading from non-Delta tables. For example, reading from a CSV table where the underlying files can change between the multiple scans.
- MERGE INTO is slow on big datasets. Think about compaction and access patterns if this happens. Having partitioning and using it in the query can help.
- A merge operation can fail if
Handling schema updates
Attempting to add data to a Delta file that has different schema ( different column names, differnt data types, etc) will cause Delta to deny the transaction and it will raise an exception (A schema mismatch detected when writing to the delta table) and will show you the current data schema and the schema of the data that you are trying to append. It becomes up to you to fix the schema before appending the data or if you want the new columns to be added to the existing schema you can choose to do Schema Evoloution by approving the new schema.
- In
merge, schema is handled the following ways:- For
update/insert, the specified target columns must exist in target - For
updateAll/insertAllsourcemust have all oftargetcolumnssourcecan have extra columns. i.e source columns can be superset- extra column are ignored by default
- If schema evolution is enabled, new columns will be added to target table
- For
TODO Table methods
- TODO Read the delta-rs docs
Table operations
See https://docs.delta.io/2.0.2/delta-update.html#language-python
- delete
- update
- merge