tags : Distributed Systems, Database, Correctness criteria, Eventual Consistency
FAQ
Strong Consistency(Linearizable) vs Sequential Consistency
- Both care about giving an illusion of a single copy.
- Sequential Consistency
- Cares about
program order P(A)executesT1andT2- then
P(B)executesT3 - Order could be:
(T1-T2)-T3,T3-(T1-T2),T1-T3-T2but notT3-T2-T1. Because this will violate order ofP(A) - There’s no global
real time order
- Cares about
- Strong consistency (Linearzability)
- Cares about
real time order P(A)executesT1andT2- then
P(B)executesT3 - Order would be:
(T1-T2)-T3
- Cares about
Strong and Weak?
Not all consistency models are directly comparable. Often, two models allow different behavior, but neither contains the other. Different consistency models fall in the spectrum of strong and weak.
- Stronger
- More restrictive consistency models
- Slower
- More time spent in doing coordination (See Consensus Protocols)
- Easier to reason about
- Weaker
- More permissive consistency models
- Faster
- Harder to reason about
Different meanings of consistency
- ACID
- Related to Database
- Satisfying application specific constraints.
- E.g. “every course with students enrolled must have at least one lecturer”
- Replication
- See Data Replication
- Replicas should be “consistent” with other replicas
- This is similar to what consistency means in CAP
- Brewer originally defined consistency as single copy
serializability. (As if we’re interacting with only one copy of the object, even though multiple things might be modifying it) - Gilbert & Lynch defined consistency as
linearizabilityof a read write register
- Different consistency models have their own meaning of consistency
Which consistency model to pick for my application?
- General rule: Pick the weakest consistency model that satisfies your needs
What’s total ordering?
- To the user it seems like they’re interacting with one single system
- In the total ordering, a read operation sees the latest write operation.
- We can always compare the logical timestamps. (i.e figure out who was last)
How are Database Locks and Database Transactions related?
Transactionsandlockscan be used together to provideserializability(isolation)Transactionsprovide atomicityTransactions+locksprovideserializability
Consistency models
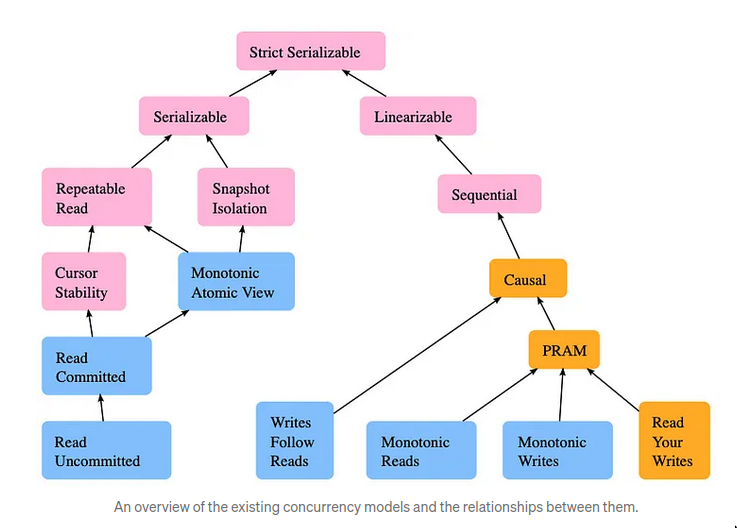
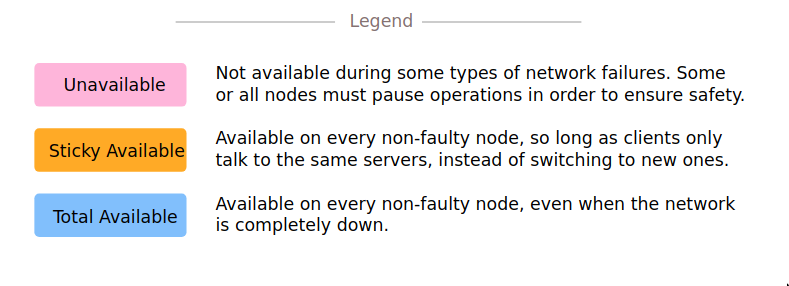
How to read this image?
- Think of the parent node as the combination of the nodes under it.
- Eg. Strict Serializable = Serializable + Linearizable
- We say that consistency model A implies model B if A is a subset of B. For example, linearizability implies sequential consistency because every history which is linearizable is also sequentially consistent.
Models
These consistency models are enabled by concurrency control (CC). You can come up with your own too. Infact many have, S3 consistency, Consistent Prefix etc.
Jespen
-
Strict Serializable
- Eg. Strict Serializable = Serializable + Linearizable
-
Linearizable
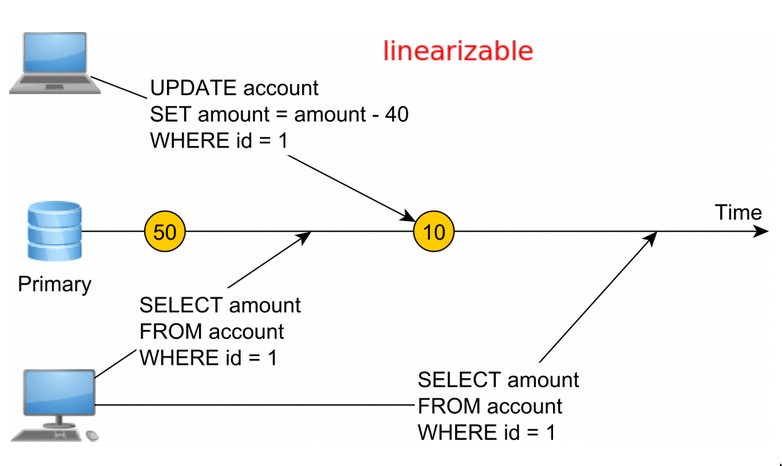
- Strong Consistency = Linearizable
- Cares about
real time order - Serializability does not take the flow of time into consideration. Linearizability implies time-based ordering.
- Modifications happen instantaneously, any read operation will see the
latest and samevalue.- Read should return the most
recentwrite - Subsequent reads should return same value, until next write
- Read should return the most
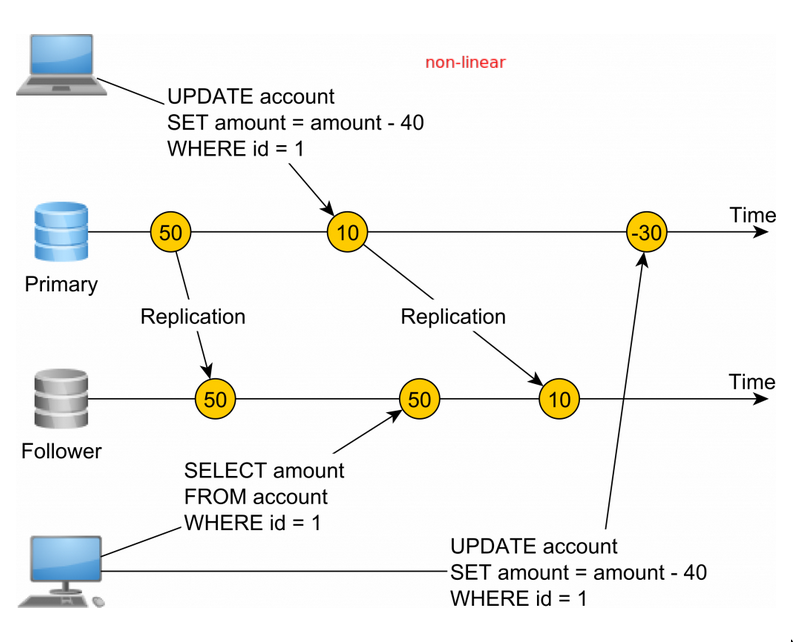
- So if the replication happened asynchronously, there will be lag and ultimately reads will not see the latest value or if replicated un-uniformly, different reads will see different values.
- So we can’t do async replication, we can’t do sync replication(too slow), so the answer is Consensus Protocols like Raft and Paxos which provide strong consistency.
-
Serializable
- AKA
one-copy serializable - Allows truly parallel execution of instructions
- Could bring in performance improvements but this also means stricter controls so that can slow things down as-well. (Tradeoff)
- Even with parallel executing transactions, the end result is same as if the transactions where executed serially.
-
Implementations
- Two Phase Locking (2PL) enables this
- Deadlock possibilities
- Serialization failures
- SSI-based (Serializable Snapshot Isolation)
- Provides performance similar to snapshot isolation and considerably outperforms strict two-phase locking on read-intensive workloads
- Transactions: Serializable Snapshot Isolation – Distributed Computing Musings
- PostgreSQL uses this
- Two Phase Locking (2PL) enables this
- AKA
-
Sequential Consistency
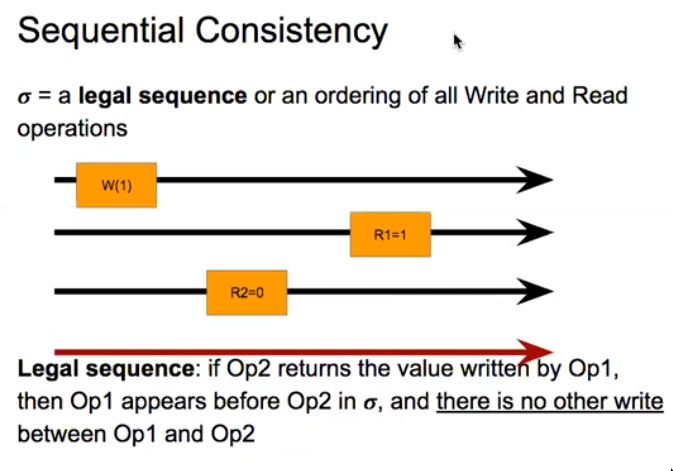
- This is weaker than Strong consistency(Linearizable)
- Cares about
program order/thread orderandlegal sequencing
-
Read your writes / Read-after-writes
- If a process writes, if it reads again it should see what it wrote
-
Monotonic Reads (Readonly)
- Time-order(fwd only), same process
- Either get the same read, else a newer read, never an older read than the first read in the process
Others
- Consistent prefix
-
S3 Consistency
- Bounded Staleness