tags : Scaling Databases, Data Engineering, Database, Distributed Systems, Concurrency Consistency Models, Raft, crdt
OG Blogpost:
FAQ
What does replication give?
The methodologies to attain this via data replication are different.
- Availability
- Fault tolerance (Durability)
- Eg. We store progress state and make sure to replicate it so that in times of crash, we can easily restart from the last checkpoint.
How does Consensus Protocols relate to Data Replication?
- There are replication architecture which use the concept of leader or there’s need of consensus, we need it then.
- When Does Consistency Require Coordination? | Peter Bailis
Retries and Idempotency
See Data Delivery
At-most-once: Send request, don’t retry, update may not happenAt-least-once: Retry request untilacknowledged, may repeat updateExactly-once: (retry + idempotence) or deduplication
Issues with idempotency
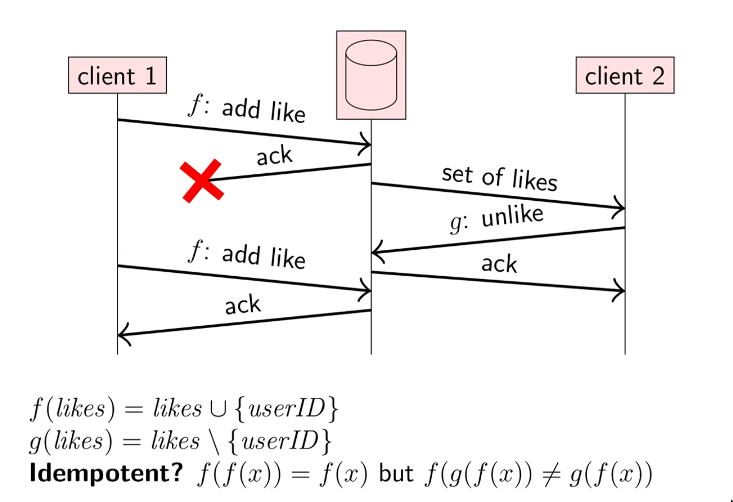
- If the functions are different eg. add & subtract on the same data, we don’t have the same gurantees
What’s a tombstone?
- When we actually don’t delete something
- But instead just mark it as deleted
- Can be GC’ed later
Failure Modes
Node failures
- Followers/Secondary: catchup recovery from log
- Leader
- Detecting leader failure: timeout based detection/Heartbeat message
- Leader Election: Node learns it’s a leader, communicated w followers
- Failover
Adding and removing data
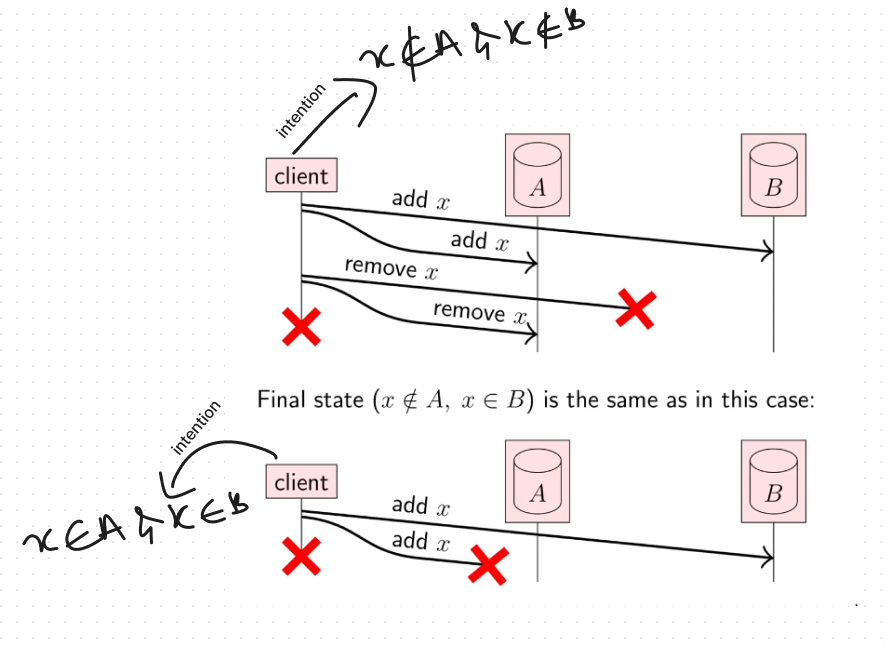
- We can solve this by using logical Clocks and timestamps!
- Every record has a logical timestamp of last write. This tells which values are newer/older.
- Without timestamp even if replicas talked among themselves, they’ll not know which one was the last write. With timestamp that’s solved with a
reconcile state/anti-entropymechanism.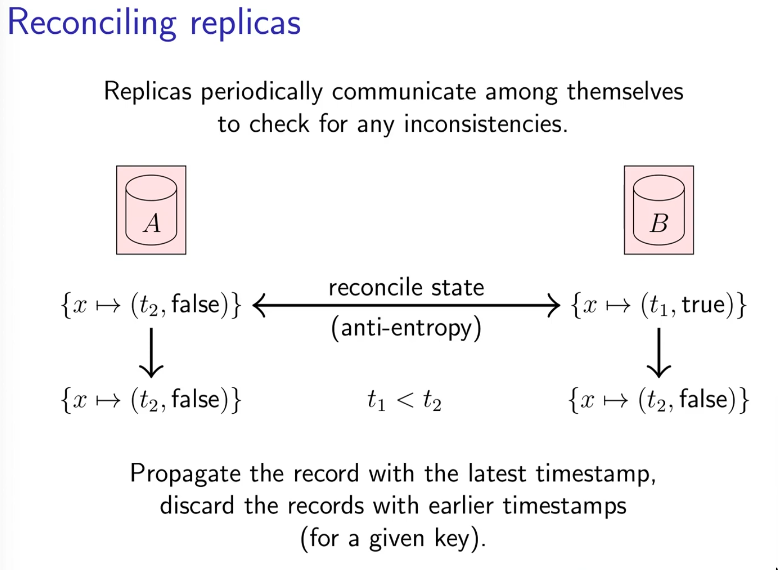
Handling writes in Replicated Systems
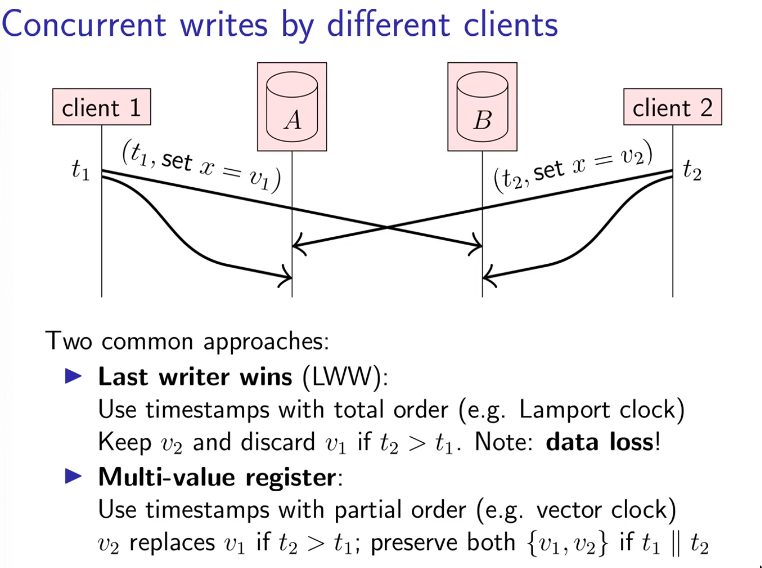
LWW (Last Writer Wins)
- We just keep the last value and discard others
- Uses Lamport Clocks (total order)
MVR (Multi Value Register)
- We want to keep all the values from all clients here
- This will keep multiple values and cause a conflict, the application code then can decide how to deal with the conflict.
- Uses Vector Clocks (partial order)
Types & Protocols
Context(as how I understand and try to fit in my mind):
- Types/methods: Uses cases and variants of replications, “types of replication” becomes what that replication allows
- Protocol: Underlying idea that can be used to implement the different “types of replication”
Replication types/methods
- These are mostly in context of database and transactional replication but can be applied to any distributed system
- NOTE: Also see PostgreSQL on the replication section.
- NOTE: There are other terminologies such as active-active etc. I am avoiding them as I don’t really want to get all that in my head rn. I am born to strike stones and create fire.
| Context | Name | Other names | What? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Database related | Logical | PG specific, but logically replicate parts of the data | |
| Streaming | Physical | When we want to stream the changes to replica/standby (In PG, its based on WAL streaming) | |
| Snapshot | |||
| Log based | Eg. In case of PostgreSQL, WAL based replication, (Streaming replication/WAL archival etc) | ||
| Transactions | Synchronous | Slow, there should be no lag in data | |
| Asynchronous | Fast, there will be some lag in data | ||
| Semi-Synchronous | In case of too many replicas, we selectively do sync for some to ensure some consistency and speed | ||
| Architecture | Leader-Follower (single writer/leader) | primary-backup, primary-replica, master-replica | Eg. PostgreSQL streaming replication |
| Leader-Follower (multi writer/leader) | Eg. CockroachDB(fake multi-writer, write is propagated to the leader) | ||
| Multi Master (true multi writer) | multi-primary | Every node is able to accept and DO the write. (There are some arch where we have RO replicas etc) | |
| Leaderless |
Following are some notes on types that I am little familiar with.
Leader-Follower
- These can be used to lower load on primary/leader and also can be used as a failover mechanism
- It’s much easier to achieve consistency with Leader-Follower setup than to use a “true multi master setup”
- If you want there to be one single leader you cannot elect a leader without either
consensusoroperator intervention
- Single writer
-
Multi writer (multiple writers accept, but only leader writes)
Not all servers accept writes, they proxy them to the leader. https://www.reddit.com/r/PostgreSQL/comments/14g0vls/framework_for_achieving_postgresql_multimaster/
Multi Master
- More often than not, when people think they “need” multi-master they actually don’t.
- Additionally: the application needs to be written for such a setup.
- People don’t seem to understand that almost no platform is automatically compatible with MM out of the box. You have to account for sequence allocation, conflict management, cumulative data types, read/write race conditions (PACELC), session / server affinity, and far more besides. I
Any replica can process a request and distribute a new state.
-
Main challenges
conflict preventionandconflict resolution- Synchronous(eager): Conflict prevention
- Async(lazy): Conflict resolution
-
Ways to implement
There are diff protocols to solve this
- Usually needs some form of distributed concurrency control must be used, such as a distributed lock manager.
- virtual synchrony model can be used aswell, chain replication etc. (See “Replication Protocols” in this page)
Replication protocols
- Now databases are also distributed systems but I wanted to separate out systems which need to replication beyond “database” needs, hence this distinction in types.
- Types of Replication - SQL Server | Microsoft Learn (Reading this I realized the names are very loosly held, don’t go by names, this is similar to Design Patterns)
- Data Replication Design Spectrum 🌟
| Name | What? | Incremental | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Streaming/Physical | |||
| Broadcast based | |||
| Chain based | |||
| Re-configuration based | |||
| State Machine Replication(SMR) | |||
| Virtual Synchrony | |||
| Hermes |
What are we taking about when we’re talking about replication protocol?
“whatever the simplest replication topology is”+“whatever the simplest membership maintenance algorithm is“
Notes on some replication protocols
-
Viewstamped Replication Protocol
- Q: This is consensus protocol or replication protocol?
- https://github.com/tigerbeetle/tigerbeetle/blob/main/src/vsr/replica.zig
- See Consensus Protocols
-
Chain based
- Chain replication is simple but it does also assume you have a consensus implementation so I sort of disqualify it from being the simplest
-
Human based
- Old-school primary backup replication is probably the simplest, as your replication topology is dictated by a human operator
TO Read
- Chain replication: https://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/fall16/cos418/docs/L13-strong-cap.pdf
- I believe MongoDB has moved to a RAFT based algorithm in their new replication protocol, CockroachDB uses a variation on it. It and PAXOS are the two of the most common distributed consensus approaches I believe.
- DDIA : Chapter 5 & 7
- https://developer.confluent.io/courses/architecture/data-replication/?s=35